How to Check CPU Power Consumption (Watts) in Real Time – Easy Methods 2025
You can check CPU power consumption in watts using tools like HWiNFO, HWMonitor, or built-in Windows features. These tools show real-time CPU wattage, voltage, and temperature to help track efficiency and performance.
In this guide, you will learn the easiest and most accurate ways to measure CPU power usage using Windows 11, BIOS settings, and trusted monitoring software.
What Is CPU Power Consumption?
CPU power consumption is the amount of electrical energy your processor consumes to perform tasks. It directly influences your computer’s speed, heat, and stability, especially during gaming or heavy workloads. Knowing how it works helps you manage temperature, improve efficiency, and pick the proper power supply.
Key Points:
- Measured in watts (W): Indicates how much power the CPU draws from your system.
- Depends on voltage and workload: Higher voltage or demanding tasks increase wattage.
- Linked to temperature: More power draw generates more heat.
- Determines PSU requirements: Helps ensure your power supply can handle peak loads.
Why Should You Monitor CPU Power Usage?
Monitoring your CPU power usage helps keep your computer stable, efficient, and protected from overheating. It is important for gamers, creators, and power users who push their systems to the limit.
Key reasons to monitor CPU power:
- Prevents overheating and throttling under heavy workloads.
- Optimizes gaming and multitasking efficiency.
- Reduces electricity use and improves energy efficiency.
- Detects cooling or hardware problems early.
- Extends CPU lifespan and ensures consistent performance.
Regular monitoring keeps your system running smoothly and protects your CPU from long-term damage.
What Factors Affect CPU Power Consumption?
CPU power consumption is not constant it changes based on how your processor operates. Understanding these factors helps you balance performance, temperature, and efficiency more effectively.
1. Clock Speed:
Higher clock speeds require more voltage and power. When a CPU runs at maximum frequency, both energy draw and heat output rise significantly.
2. Number of Cores and Threads:
More cores mean greater power usage. When multiple cores or threads are active, total consumption increases, especially during gaming, rendering, or multitasking.
3. Voltage Settings:
Voltage directly affects power draw. Even small voltage increases can cause large jumps in wattage, which is why overclocked CPUs consume more power and generate more heat.
4. Workload Type:
Demanding tasks push the CPU closer to its maximum TDP, while lighter workloads keep it at lower wattage levels.
5. Temperature and Cooling:
A hot CPU becomes less efficient. Poor cooling or high ambient temperatures can lead to performance drops and increased power draw.
6. Power Plan and BIOS Settings:
Windows Power Plans and BIOS features like Intel Turbo Boost or AMD Precision Boost influence how aggressively your CPU manages power.
7. Manufacturing Process and Architecture:
Modern CPUs built on smaller processes, such as 5nm or 7nm, are more efficient, delivering better performance per watt than older architectures.
By understanding factors such as clock speed, voltage, and cooling, you can better manage your CPU power consumption. Next, we will compare how this differs between laptops and desktops.
Laptop vs Desktop CPU Power Consumption:
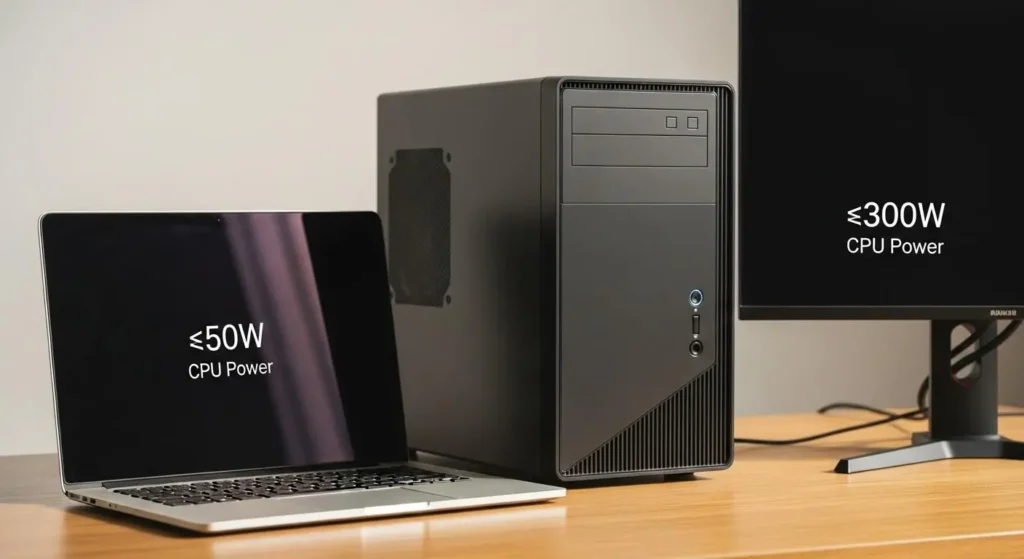

Laptop CPUs are designed for power efficiency and longer battery life, typically consuming between 15 and 45 watts under load. They use dynamic voltage control, advanced thermal management, and low-power sleep states to minimize heat while maintaining smooth performance ideal for portable and energy-efficient computing.
Desktop CPUs, in contrast, are built for maximum performance and sustained workloads, often drawing 65 to 250 watts depending on usage. Their larger cooling systems and higher power limits allow consistent turbo speeds and stable performance without throttling.
Also Read: Laptop vs Desktop CPU Performance – Complete Guide 2025!
How to Check CPU Power Consumption in Windows 11?
To check CPU power consumption in Windows 11, you can use built-in tools like Task Manager for basic power usage insights or advanced utilities such as HWiNFO, HWMonitor, Intel XTU, AMD Ryzen Master, and Open Hardware Monitor for accurate real-time wattage (W), voltage, and temperature readings. These tools help you track CPU performance, efficiency, and power behavior under different workloads.
Check CPU Power in Task Manager:
Task Manager offers a quick overview of CPU activity and estimated power usage.
Steps:
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager.
- Go to the Performance tab and select CPU.
- Open the Processes tab, right-click the column header, and choose Columns. From the list, check Power Usage and Power Usage Trend to view real-time power data.
- Observe how your CPU power behavior changes with workload.
Note: Task Manager does not show exact wattage. It only provides an estimated power usage level. For precise watt readings in watts (W), use tools like HWiNFO or HWMonitor
Use HWiNFO for Detailed Analytics:
HWiNFO delivers advanced sensor-level data and long-term logging.
Steps:
- Install and run HWiNFO64, then select Sensors Only mode.
- Scroll to find CPU Package Power, Core Power, and VRM Efficiency.
- Enable logging or view graphs to analyze power trends over time.
Use HWMonitor to Measure CPU Wattage:
HWMonitor provides accurate real-time wattage for all components.
Steps:
- Download and install HWMonitor from its official website.
- Open the app and locate CPU Package Power (W) under your processor name.
- Compare idle vs. load values to gauge power efficiency.
- Note voltage and temperature readings for full context.
Intel XTU for Intel CPU:
For Intel processors, Intel Extreme Tuning Utility (XTU) lets you both monitor and fine-tune CPU power limits.
Steps:
- Download Intel XTU from Intel’s website.
- Open it and navigate to the Advanced Tuning tab.
- Review Package TDP, Core Power, and Turbo Boost Power Max.
- Use the graphs to monitor real-time power fluctuation under load.
Ryzen Master for AMD CPU:
AMD Ryzen Master gives precise, real-time control and monitoring for Ryzen CPUs.
Steps:
- Install and open AMD Ryzen Master.
- Look for PPT (Package Power Tracking), TDC, and EDC values.
- Compare readings at idle and under stress load.
- Adjust performance modes for better power efficiency.
Using Open Hardware Monitor:
This lightweight tool tracks CPU power, temperature, and voltage in real time.
Steps:
- Install and open Open Hardware Monitor.
- Expand your CPU section to view Power (W) readings.
- Use the logging option to record power data over time.
- Review logs to find average, minimum, and maximum power use.
How to Check CPU Power Consumption in BIOS or UEFI?
You can check CPU power consumption in the BIOS or UEFI by entering your motherboard’s hardware monitoring section, where real-time wattage and voltage readings are displayed. This method doesn’t require booting into Windows and often provides more accurate results since data comes directly from the motherboard’s sensors.
Steps:
- Restart your PC and press Del or F2 during startup to enter the BIOS or UEFI.
- Navigate to the Hardware Monitor, PC Health, or Monitoring tab.
- Look for parameters such as CPU Voltage, CPU Power (W), or Package Power.
- Review the real-time wattage values while the system is idle.
- Exit BIOS after checking your readings.
BIOS-based power readings are often more accurate than software tools because they come straight from the motherboard’s power controller, with no interference from background applications.
How to Check CPU Power While Gaming or Under Load?
You can check CPU power consumption during gaming or heavy workloads using monitoring tools like MSI Afterburner or OCCT, which display real-time wattage, temperature, and clock speeds directly on-screen. This helps verify performance, cooling efficiency, and power draw under stress.
Using MSI Afterburner or OCCT:
Both tools allow live tracking of CPU behavior, but they offer different advantages.
Steps:
- Download and install MSI Afterburner or OCCT from their official websites.
- Launch the tool and enable the on-screen display (OSD) or logging feature.
- Start a CPU-intensive game or run a stress test to simulate a heavy load.
- Monitor CPU wattage, temperature, and frequency in real time.
- Compare idle vs full-load results to measure performance efficiency.
What Is Normal CPU Power Consumption in Watts?
CPU power consumption in watts depends on workload and CPU type. At idle, most modern CPUs use between 5W and 30W. During gaming or heavy tasks like rendering, power draw can increase sharply, often reaching 65W to 250W depending on the processor.

Below is a realistic comparison of average idle and load power usage (in watts) for popular Intel and AMD CPUs.
| CPU Model | Idle Power (W) | Load Power (W) | Notes |
| Intel Core i5-13600K | 12W | 125W | Balanced power and performance |
| Intel Core i9-14900K | 18W | 250W | High-end chip with strong load power |
| AMD Ryzen 5 7600 | 10W | 90W | Efficient 6-core processor |
| AMD Ryzen 9 7950X | 20W | 230W | Great for multitasking, runs hotter |
| Intel Core i3-12100F | 8W | 65W | Low-power entry-level CPU |
Note: Actual CPU power consumption can vary depending on motherboard, BIOS power limits, cooling solution, and workload intensity.
Overall, CPU power consumption rises sharply under load, with high-end models using much more energy than efficient mid-range options.
You may also like: Is 50°C Safe for CPU at Idle? – Expert Guide 2025!
How to Reduce CPU Power Consumption?
Lowering CPU power consumption helps cut heat, extend hardware life, and boost energy efficiency, especially during long gaming or multitasking sessions.
Tips to Lower CPU Power Draw:
- Undervolt your CPU: Use tools like Intel XTU or AMD Ryzen Master to safely reduce the CPU voltage without sacrificing stability.
- Enable Balanced Power Mode: Open Control Panel, select Power Options, and set Balanced to optimize performance and energy use.
- Clean dust from coolers: Better airflow keeps temperatures low and prevents wasted power.
- Limit background apps: Close unused software and disable startup programs to reduce CPU load.
- Disable Turbo Boost (optional): This limits maximum power draw during demanding tasks.
- Update BIOS and chipset drivers: Improves power regulation and overall system efficiency.
- Improve case cooling: Strong airflow keeps your CPU stable and prevents thermal throttling.
Even small changes like undervolting or cleaning your system can noticeably reduce total power draw without affecting daily performance.
FAQs:
1. Does higher wattage mean better performance?
No. Performance depends more on efficiency, architecture, and cooling than raw wattage.
2. Is TDP the same as actual power consumption?
No. TDP (Thermal Design Power) defines heat output under standard conditions, not real-time watt usage.
3. Does idle power usage affect CPU health?
Yes. Continuous high voltage, even when idle, can slightly reduce CPU lifespan over time.
4. Does gaming always use maximum CPU power?
Not always. Most games use only part of your CPU’s cores, so power draw varies by title and settings.
5. Does undervolting reduce performance?
When done correctly, undervolting improves thermals and efficiency without reducing processing speed.
Conclusion:
Monitoring your CPU power consumption is key to keeping your system fast, cool, and efficient. With tools like HWMonitor, HWiNFO, or your BIOS, you can easily check real-time wattage and detect any unusual power spikes early. Regularly updating your BIOS and chipset drivers, managing background tasks, and maintaining proper cooling will help ensure stable performance, lower heat output, and a longer CPU lifespan.
If your CPU shows unusually high wattage at idle, undervolting and BIOS tuning can significantly improve efficiency.