How Many Threads Does My CPU Have? – Discover CPU Power 2025!
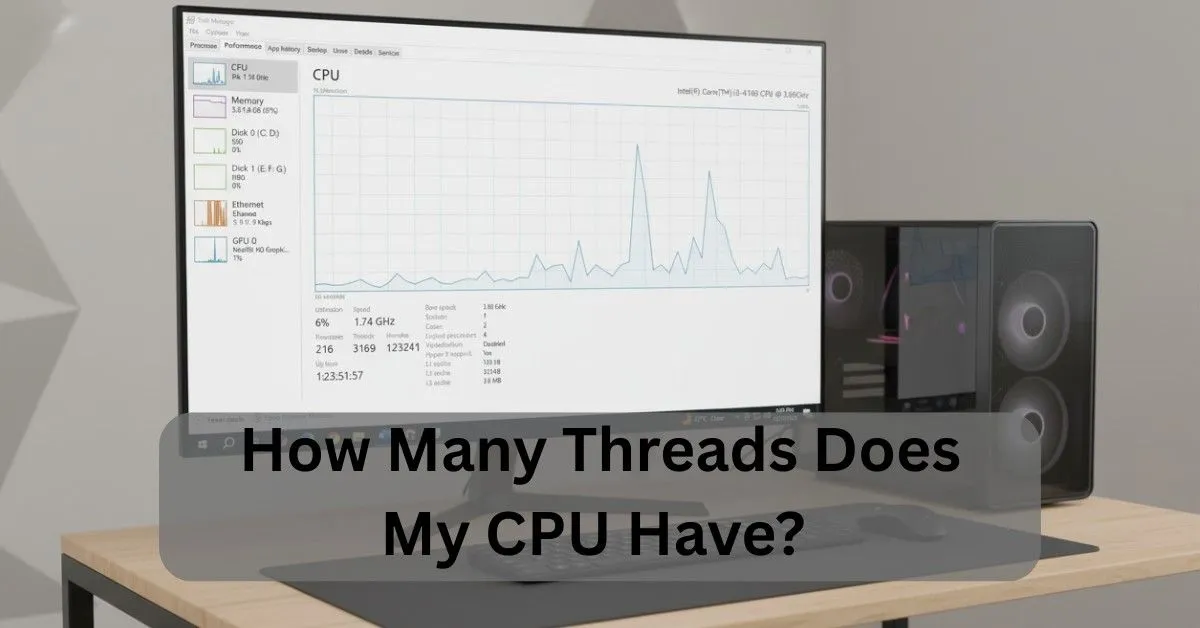
Your CPU thread count shows how many tasks it can process at once using technologies like Hyper-Threading or SMT, which boost multitasking and speed. You can easily check your CPU threads in Task Manager on Windows or via Terminal on Mac and Linux.
Stay connected as we explore easy ways to check how many threads does my CPU have. Learn how to view your CPU’s thread count on Windows, Mac, and Linux effortlessly.
CPU Cores and Threads:
Understanding CPU cores and threads helps you see how your processor handles performance and multitasking. A CPU’s cores and threads determine how many tasks it can handle at the same time, affecting everything from gaming to professional workloads.
What Is a CPU Core?
A CPU core is the physical unit that performs processing tasks. Each core can independently execute programs and calculations, so more cores generally mean better multitasking and improved performance in software that supports multiple cores.
What Is a CPU Thread?
A CPU thread is a virtual sequence of instructions that a core can handle. Modern CPUs use technologies like Hyper-Threading or SMT to allow each core to run multiple threads simultaneously, effectively increasing the CPU’s efficiency without adding more physical cores.
Why Does Thread Count Matter?
Your CPU thread count decides how many tasks it can handle at once. More threads mean smoother multitasking, better application performance, and improved efficiency in software that supports multiple threads. This is key for both everyday tasks and demanding workloads.
Thread count matters especially for gaming, video editing, and running multiple applications at the same time. Higher thread numbers allow your CPU to divide workloads efficiently, reduce lag, and improve overall responsiveness. Even background tasks run more smoothly, making the system feel faster and more capable under heavy use.
How To Check CPU Threads in Windows?
Here’s how you can quickly check your CPU thread count on Windows.
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager.
- Click Performance.
- Select CPU from the left pane.
- Read Cores physical and Logical Processors threads.
How To Check CPU Threads in Linux?
Open a terminal and run lscpu. Check the CPU or Threads per core fields. CPU shows the total logical processor threads.
Quick alternative: run nproc to print the total available threads.
How To Check CPU Threads on Mac?
Open Terminal and run:
sysctl -n hw.logicalcpu
This command shows the total number of logical processor threads.
Or open About This Mac, then System Report, and select Hardware to view cores and processor details.
Also Read: How to Reduce CPU Usage while Gaming? – Optimize Gaming 2025!
Which CPUs Have How Many Threads?
Here is a quick comparison of popular Intel and AMD CPUs and how their cores and threads stack up for gaming and productivity. The table lists each model’s cores and threads, helping you compare multitasking power and choose the best CPU for gaming, productivity, or professional workloads.
| Vendor | Generation | Model | Cores | Threads | |
| Intel | 10th Gen | Core i7- 10700K | 8 | 16 | |
| Intel | 11th Gen | Core i9-11900K | 8 | 16 | |
| Intel | 12th Gen | Core i9-12900K | 16 | 24 | |
| Intel | 13th Gen | Core i9-13900K | 24 | 32 | |
| Intel | 14th Gen | Core i9-14900K | 24 | 32 | |
| AMD | Ryzen 1000 | Ryzen 7 1700 | 8 | 16 | |
| AMD | Ryzen 2000 | Ryzen 7 2700X | 8 | 16 | |
| AMD | Ryzen 3000 | Ryzen 7 3700X | 8 | 16 | |
| AMD | Ryzen 5000 | Ryzen 7 5800X | 8 | 16 | |
| AMD | Ryzen 9000 (Zen 5) | Ryzen 9 9950X3D | 16 | 32 |
Tip: Want to verify cores and threads for any CPU model? Visit the official pages below:
- Intel CPU Search: Click here to find your Intel CPU
- AMD CPU Search: Click here to find your AMD CPU
Bookmark these pages to quickly verify cores and threads for any future CPU upgrade.
Also Read: Laptop vs Desktop CPU Performance – Complete Guide 2025!
Why is My CPU Thread Count Lower Than Expected?

Sometimes users notice fewer threads than anticipated. Understanding how many threads my CPU has helps identify the cause. Various factors like system settings, software, and CPU design can affect the visible thread count.
BIOS/UEFI Settings:
Some BIOS or UEFI configurations may have Hyper-Threading/SMT disabled. Enabling it can unlock the expected logical threads on your CPU.
Operating System Limitations:
Certain OS versions, especially older ones, may not recognize all threads. Updating or using a modern OS often resolves the issue.
CPU Architecture & Model:
Not all CPUs support multiple threads per core. Entry-level or older CPUs may physically have fewer threads than modern high-performance models.
Virtualization or Software Tools Issue:
Some monitoring tools or virtual machines may not report threads accurately. Using official OS utilities provides correct thread information.
Tip: Check your BIOS settings and make sure Hyper-Threading or SMT is enabled. Also, ensure your operating system recognizes all cores to see the correct thread count.
Does Thread Count Affect Gaming or Multitasking?
Thread count can impact how efficiently your CPU handles multiple tasks at the same time. For multitasking, higher thread numbers allow your system to run several applications smoothly, reduce lag, and improve overall responsiveness. Gamers may notice smoother performance when streaming or running background apps simultaneously.
Knowing your CPU’s thread count helps you predict gaming and multitasking performance. More threads allow modern games, video editing, and productivity software to divide workloads effectively, ensuring faster processing and better system stability under heavy workloads.
You may also like: How Much CPU Usage is Normal? – Optimize CPU 2025!
Can I Increase CPU Threads?
You cannot add extra threads beyond what your CPU is designed for. However, understanding how many threads my CPU has helps me ensure features like Hyper-Threading or SMT are enabled in BIOS/UEFI. These settings let each core run multiple threads for better efficiency, but the total count still depends on your CPU’s design.
What is Hyper Threading And SMT?
Hyper-Threading (Intel) and Simultaneous Multi-Threading (SMT – AMD) allow each CPU core to handle multiple threads at once. This boosts multitasking and improves performance in applications and games, without adding extra physical cores.
Hyper-Threading For Intel CPUs:
Hyper-Threading lets each Intel core run two threads simultaneously. This doubles the number of logical processors, enabling smoother multitasking and better performance in multi-threaded applications.
Simultaneous Multi-Threading For AMD CPUs:
SMT is AMD’s version of Hyper-Threading, allowing each core to execute multiple threads at the same time. It improves CPU efficiency, especially for gaming, rendering, or video editing, by making full use of each physical core.
Conclusion:
Understanding how many threads does my CPU have helps you measure your system’s multitasking power. A higher thread count means smoother gaming, faster rendering, and better performance. Check your CPU threads today, enable Hyper-Threading or SMT if supported, and unlock your processor’s full performance potential.
FAQ’s:
1. How Many Threads Should My CPU Have?
It depends on your workload. For general tasks, 4 to 8 threads are sufficient, while heavy multitasking, gaming, or content creation may benefit from 16 to 32 threads or more.
2. Are More Threads Better For Gaming?
Not always do most games rely on single-core speed. More threads help if you run background apps or stream while gaming.
3. Do more threads always mean better CPU performance?
More threads do not always mean better performance, it depends on how well your software or games use those extra threads.
4. Does Disabling Hyper-Threading Reduce Threads?
Yes, disabling Hyper-Threading (Intel) or SMT (AMD) reduces the number of logical threads available, though physical cores remain the same.
5. Can Thread Count Reveal GPU Bottleneck?
No, thread count only reflects CPU parallelism. GPU bottlenecks depend on graphics card performance, memory bandwidth, and workload, not CPU threads.