What Does Ti Mean in GPU? – NVIDIA Ti vs Non-Ti Explained 2025!

In NVIDIA’s graphics card lineup, “Ti” stands for Titanium, a branding term for a faster, more powerful version of a standard GPU. It does not refer to the physical material of the graphics card. Ti models usually deliver higher FPS, better ray tracing, and longer usability than non-Ti cards, but at a higher price.
This guide explains their meaning, evolution, and real-world value in 2025.
How Ti GPUs Are Different From Non-Ti Models:
Ti GPUs are upgraded versions of standard NVIDIA graphics cards, designed to deliver higher performance within the same generation. Compared to non-Ti models, Ti variants usually feature more CUDA cores, higher boost clock speeds, and increased VRAM, which results in better gaming FPS, stronger ray-tracing performance, and smoother handling of demanding workloads. However, these gains also come with higher power consumption and cost.
GPU performance increases often put extra load on the processor, making CPU temperature and cooling more important.
Also Read: Is 50°C Safe for CPU at Idle? – Expert Guide 2025!
History and Evolution of the NVIDIA Ti Suffix:
To provide more powerful GPUs within a single generation, NVIDIA introduced the Ti suffix. Over time, Ti models established themselves as a stable upgrade tier, offering improved specifications without the cost of flagship cards.
Early NVIDIA Ti Suffix Models:
NVIDIA first introduced the “Ti” designation in 2001 with the GeForce 3 Ti series (Ti 200 and Ti 500) and the GeForce 2 Ti. These early models used higher clock speeds and optimized chips to deliver better performance than base versions, establishing Ti as a symbol of “Titanium” that evoked premium strength and reliability.

This strategy also allowed NVIDIA to maximize silicon yields by binning higher-quality dies for Ti variants, improving efficiency while offering enthusiasts better performance.
Ti Through the Generations:
GeForce 4 (2002): Ti 4200, 4600, and flagship Ti 4800
GeForce FX (5000): Only minimal Ti brand usage.
GeForce 6/7: Selective mid-range Ti upgrades.
GTX Era (20082018): The known models include GTX 1070 Ti and 1080 Ti.
RTX Era (2018 onwards): High-end Ti models, including RTX 2080 Ti, 3080 Ti and 4070 Ti.
Ti vs Non-Ti Performance Difference:
Ti graphics cards come with higher specifications than their non-Ti counterparts. Common upgrades include:
- More CUDA cores for improved parallel processing
- Higher boost clock speeds for better in-game performance
- Increased VRAM capacity for high-resolution textures
- Wider memory bus in some models for higher bandwidth
These improvements typically result in 15–30% better performance depending on the workload.
| Feature | Non-Ti (RTX 4070) | Ti (RTX 4070 Ti) |
| CUDA Cores | 5,888 | 7,680 |
| VRAM | 12GB GDDR6X | 16GB GDDR6X |
| Boost Clock | 2475 MHz | 2610 MHz |
| TDP | 200W | 285W |
Actual performance gains vary depending on the game, resolution, and cooling design.
According to NVIDIA’s official specifications, Ti models feature higher core counts and memory configurations that explain these performance gains.
What Is the Difference Between Ti and Super in NVIDIA?
NVIDIA also uses the “Super” label for refreshed models released mid-generation. Super variants typically offer modest performance and efficiency improvements over the base version, often filling gaps in NVIDIA’s lineup.
Ti cards usually represent a higher-tier upgrade, offering larger hardware boosts such as more CUDA cores or higher power limits. In some generations, Super and Ti models overlap, but Ti generally denotes the more premium option.
For example, some GPUs combine both labels, indicating a more substantial upgrade than either designation alone.

Source: Amazon.com
Ti GPU Performance in the RTX 40 Series:
In the RTX 40 series, Ti GPUs deliver noticeably higher performance than standard models, making them well-suited for 1440p gaming and entry-level 4K workloads. These cards typically feature higher core counts, higher clock speeds, and wider memory configurations.
Ti Super variants introduce additional enhancements designed for creators and demanding workloads, delivering approximately 8–10% higher performance and improved long-term value when paired with high-end CPUs, such as the Ryzen 7 7800X3D.
Is a Ti GPU Worth the Extra Cost?
Ti GPUs usually cost more than standard models, often by 20–40%, depending on the generation and current market prices. In real use, that extra money brings better gaming performance, smoother ray tracing, and a card that tends to stay relevant for longer.
From a value perspective, Ti models often make more sense for users planning to keep their GPU for several years.
For most gamers, the higher price makes sense for 1440p or 4K gaming, content creation, or long-term builds. For basic 1080p gaming or on a tight budget, though, a regular non-Ti GPU is often the smarter choice.
Also Read: Best Ryzen CPU for Plex Server (1080p & 4K) – 2025
Latest Ti Variants in RTX 50 Series (2025 Updates):
NVIDIA continues using the Ti branding with its Blackwell-based RTX 50 series, launched in early 2025. The RTX 5070 Ti stands out as an efficient upper-midrange option, featuring GDDR7 memory, improved power efficiency, and support for DLSS 4.
NVIDIA typically rolls out higher-end Ti variants later in the generation, based on market demand.

Image Source: Amazon.com
How Ti GPUs Perform in Gaming Laptops:
In laptops, Ti GPUs like the RTX 4070 Ti Laptop GPU offer around 10–20% better performance than non-Ti mobile versions, mainly due to higher power limits and better tuning. Strong cooling designs (such as ROG Strix) matter most. Battery life is shorter, but hybrid and eco modes help manage power. However, actual performance still depends heavily on the laptop’s cooling and power limits.
Ti for Gaming vs Content Creation?
Ti GPUs deliver higher FPS and smoother ray tracing in games, while also speeding up creative workloads. In apps like Blender, Premiere Pro, and DaVinci Resolve, Ti models can cut render and export times by around 20–25%. Their stronger CUDA and Tensor cores also benefit AI-based tools.
Common Ti GPU Issues and How to Fix Them:
Ti GPUs may experience overheating, which is often resolved by undervolting or improving airflow, while driver crashes often require a clean driver reinstall. When buying a used Ti card, always check VRAM health. Most NVIDIA Ti GPUs come with a standard 3-year warranty for added peace of mind. Most of these issues are manageable and don’t reflect a problem with the GPU itself.
Many GPU-related errors are caused by airflow or fan issues rather than the graphics card itself.
Also Read: CPU Fan Not Spinning? Quick Fixes & Causes (2025 Guide)
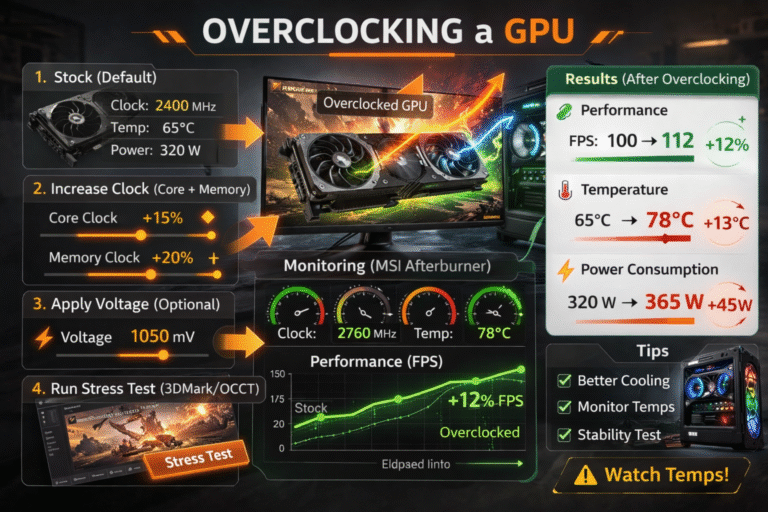
Expert Overclocking Tips for Ti?
Ti cards usually have good overclocking headroom. Using tools like MSI Afterburner, a safe +100 to +150 MHz core boost is common on air cooling. With better cooling or water-cooling, Ti GPUs can gain up to 8–10% extra performance while remaining stable and efficient.
Ti GPU Alternatives From AMD and Intel:
AMD and Intel don’t use the “Ti” branding, but they do offer GPUs that compete closely with NVIDIA’s Ti models in terms of performance and value.
AMD Alternative:
The Radeon RX 7900 XT delivers performance comparable to NVIDIA’s upper-midrange Ti cards, especially in rasterized gaming. It often offers better price-to-performance for non-ray-traced workloads.
Intel Alternative:
Intel’s Arc A750 and A770 focus more on value and modern features like AV1 encoding and AI acceleration. While they don’t directly match Ti-level performance, they are solid options for budget-conscious builds.
FAQs:
1. What does Ti stand for in NVIDIA GPUs?
Ti stands for Titanium, a label NVIDIA uses for higher-performance GPU versions.
2. Is a Ti GPU better than a non-Ti GPU?
Yes, Ti models usually deliver 15–30% better performance due to upgraded hardware.
3. What is the difference between Ti and Super GPUs?
Ti is a premium upgrade, while Super is a mid-generation performance refresh.
4. Is a Ti GPU worth the extra cost?
Yes for serious gaming and creative work; casual users may not need it.
5. Does Ti mean the GPU is made from titanium?
No, Ti refers only to the branding and does not indicate the card’s material.
Conclusion:
What does Ti mean in GPU? A Titanium upgrade for speed, cores, and endurance. From its early history to the RTX 50 Ti era in 2025, the Ti branding continues to power high-end gaming and creative workloads. If you are pushing modern games or creative workloads, a Ti GPU can feel like a noticeable step up rather than a minor upgrade.