Intel GPU Drivers: Complete Download, Update & Troubleshooting Guide
Intel GPU drivers control how your integrated or Arc graphics communicate with Windows or Linux. Installing the correct Intel GPU drivers improves performance, fixes display bugs, and prevents crashes.
Whether your Intel graphics is crashing, outdated, or underperforming, this guide walks you through the safest solutions step by step.
What Are Intel GPU Drivers?
Think of Intel GPU drivers as the bridge between your hardware and software. They tell your integrated or discrete graphics processor how to render images, videos, and games efficiently. Without proper drivers, you might face laggy performance or even system crashes.
Intel offers these for their integrated GPUs in Core processors and discrete options like the Arc series. In real-world setups, I have seen outdated drivers cause everything from flickering screens to poor frame rates in simple tasks like browsing.
Why Update Your Intel GPU Drivers:
Updating Intel GPU drivers is important to maintain smooth graphics performance, system stability, and compatibility with modern software. New driver versions also help prevent crashes and display issues caused by outdated drivers.
Performance Improvements:
The latest Intel GPU drivers improve FPS, reduce stuttering, and enhance video playback and gaming performance. They also optimize hardware acceleration and power efficiency.
Bug Fixes & Stability:
Driver updates fix common issues such as screen flickering, black screens, crashes, and random freezes. This results in a more stable and reliable system.
Compatibility with New Windows Updates:
Windows updates can cause conflicts with older graphics drivers. Updating Intel GPU drivers ensures full compatibility with the latest Windows versions and DirectX updates.
Security Enhancements:
Intel GPU driver updates include security patches that fix known vulnerabilities. Keeping drivers updated helps protect your system from potential exploits and instability.
Types of Intel GPUs: From Integrated to Discrete
Intel offers a range of GPUs, each with tailored drivers. Here’s a breakdown:
Integrated Graphics (iGPUs):
Built into processors like the Intel Core series. Examples include UHD Graphics for basic tasks and Iris Xe for light gaming or creative work. Drivers focus on efficiency and low power use.
Discrete Graphics (dGPUs):
Standalone cards like the Intel Arc series (A770, B580). These handle heavy workloads like 4K editing or AAA games, with drivers emphasizing performance boosts and ray tracing support.
Legacy Models:
Older HD Graphics in 6th-10th gen processors. Drivers are still available but receive fewer updates, prioritizing stability over new features.
Pro and Data Center GPUs:
Like Arc Pro for workstations, drivers include enterprise tools for reliability in professional environments.
Intel GPU drivers are optimized differently depending on whether you use integrated, discrete, or legacy graphics.
| GPU Type | Use Case | Driver Focus | Example Models |
| UHD Graphics | Everyday computing, streaming | Power efficiency, basic rendering | Core i3/i5 (11th-14th gen) |
| Iris Xe | Creative apps, casual gaming | Enhanced visuals, AI features | Core Ultra series |
| Arc Discrete | Gaming, content creation | High FPS, ray tracing | Arc A750, B580 |
| HD Legacy | Older systems | Compatibility fixes | 7th-10th gen processors |
If you are unsure which category your GPU falls into, follow the identification steps below.
How to Identify Intel GPU Model?
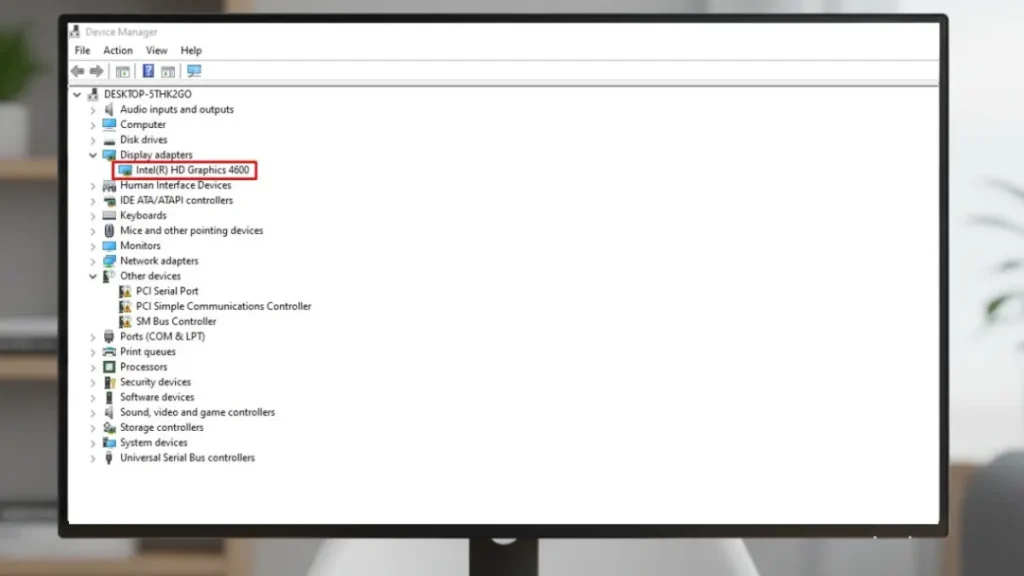
Knowing your exact GPU model ensures you download the proper drivers. It is straightforward, but many skip this and end up with mismatches.
- On Windows: Right-click the Start button, select Device Manager. Expand “Display adapters,” and your Intel GPU will show up, like “Intel UHD Graphics 770.”
- Check via Command Prompt: Type “dxdiag” in the search bar, hit Enter. Go to the Display tab for detailed specs, including driver version.
- On Linux: Open a terminal and run “lspci | grep VGA.” This lists your graphics controller, such as “Intel Corporation Iris Xe Graphics.”
- Use Intel’s Tool: Download the Intel Processor Identification Utility from their site, which scans and reports your GPU details automatically.
If you have ever upgraded your CPU, double-check this; new processors often come with updated integrated graphics.
Suggest image: Screenshot of Device Manager showing an Intel GPU entry.
Where to Download Intel GPU Drivers Safely?

Image Source: Intel Official Website. Used for educational and informational purposes.
Head straight to the official Intel Download Center. Search for your model, select your OS, like Windows 11, and grab the latest .exe or .zip file. Avoid shady third-party sites to dodge malware. For legacy support on older generations like 11th-14th Core, Intel has split drivers into a separate branch.
Pro tip: Bookmark the site for quick access. If you are on Linux, check distro-specific repos, but this guide focuses on Windows for US users. At the end of this section, learn more about safe GPU temperature ranges.
How to Install Intel GPU Drivers Automatically:
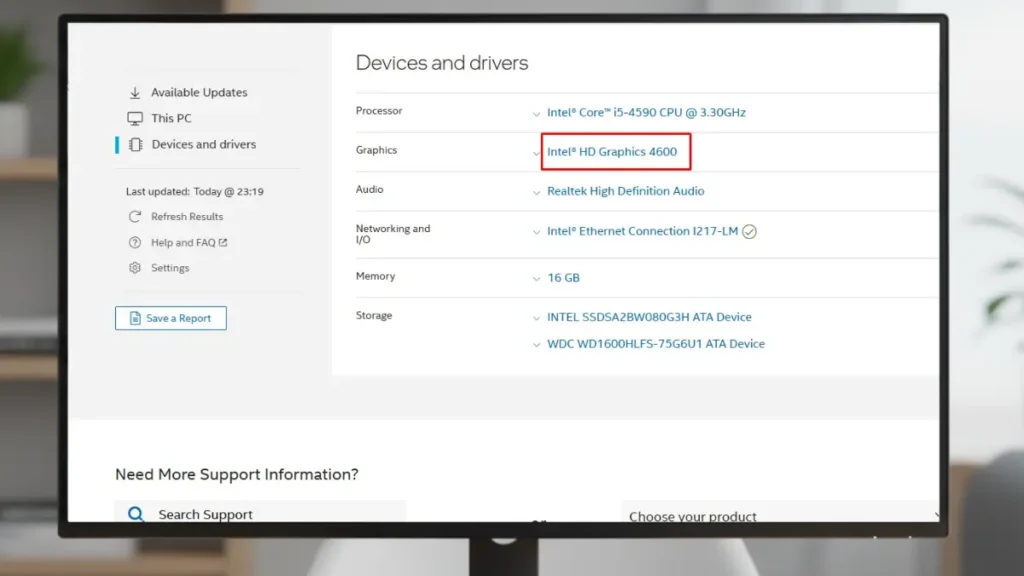
Image Source: Intel Official Website. Used for educational and informational purposes.
- Install Intel Driver & Support Assistant
- Run a scan
- Review recommended driver updates.
- Click Download & Install
- Restart your system
Automatic updates ensure compatibility and reduce installation errors for beginners.
How to Install Intel GPU Drivers Manually:
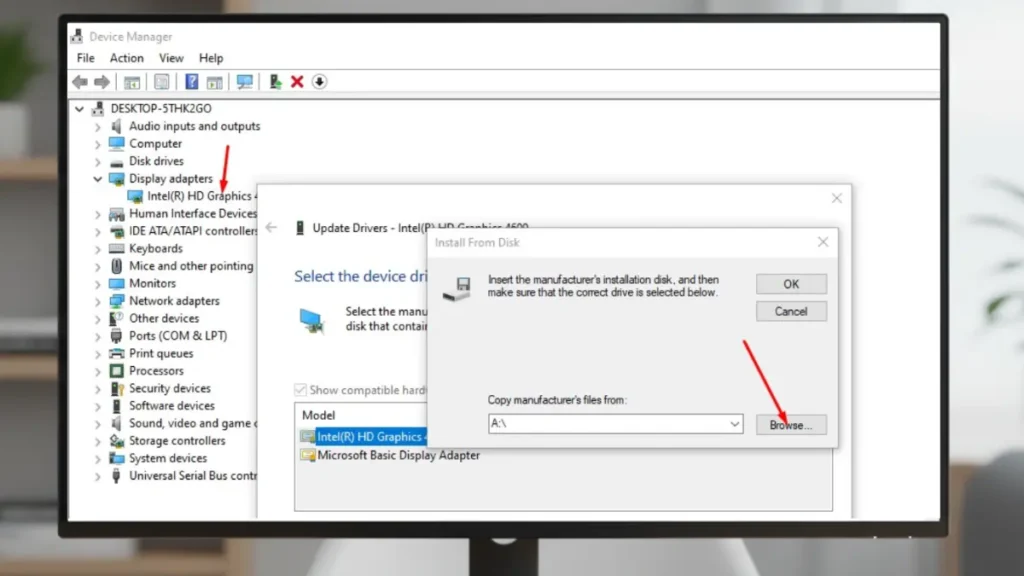
- Identify your Intel GPU model
- Download the correct driver for your Windows version.
- Extract the files
- Run the installer or update via Device Manager.
- Restart your PC
Pro tip: Always create a system restore point before manual installation, as it can save you a lot of headaches.
Common Installation Issues and Fixes?
Intel drivers are solid, but issues pop up. Here’s how to tackle the frequent ones.
Black Screen or Freeze During Install:
- Boot into Safe Mode
- Uninstall old driver via Device Manager
- Retry installation
BSOD (Blue Screen of Death):
Update Windows fully; an outdated OS causes this. Use Intel’s diagnostic tool to scan for errors.
Known Issues Warning in Games:
Installing the latest driver from Intel ignores outdated versions. Check app compatibility too.
Slow Performance or Lag:
Clean install and disable unnecessary background apps. For Arc GPUs, enable Resizable BAR in BIOS.
Driver Not Detected:
Verify hardware in BIOS; sometimes a loose connection or faulty GPU is the culprit.
In most reported cases, performing a clean Intel GPU driver installation resolves display glitches and crash-related issues, especially after major Windows updates.
Check your GPU health and troubleshoot issues.
How to Update Intel GPU Drivers Regularly?
Set the Support Assistant to check monthly. Or manually visit the site and compare versions. Windows Update sometimes pushes them, but it’s not always the newest. In gaming rigs, update before big releases to avoid crashes. Real scenario: A friend skipped an update and faced stuttering in new titles until he refreshed.
How to Uninstall or Rollback Intel GPU Drivers?
Need to revert? In Device Manager, right-click your GPU, select Uninstall device, then restart. Windows reinstalls a basic version. For rollback, use the driver’s properties tab. Tools like DDU handle deep cleans.
Many users overlook Windows updates, even though they often work alongside driver updates to resolve graphics issues.
Optimizing Performance with Intel GPU Drivers:
To get the most out of Intel Graphics Command Center, set Anisotropic Filtering to 16x for sharper textures without affecting FPS. Medium Anti-Aliasing smooths edges in games, while choosing Maximum Performance in Power Mode boosts GPU clock speeds during demanding tasks.
Adjusting Graphics Settings:
Prose about Anisotropic Filtering, Anti-Aliasing, Power Mode (table → prose).
Monitoring Temperatures:
Prose about keeping GPU under 80°C, cleaning dust, and hardware acceleration. Safe GPU temperature ranges for Intel and AMD graphics.
Advanced Performance Tweaks:
Prose about undervolting, MSI Afterburner, and benchmarking.
Intel GPU Drivers for Gaming and Productivity:
In games, drivers unlock features like XeSS upscaling on Arc. Test in titles like Fortnite, which is more GPU-heavy these days. For work, they speed up video editing in Premiere Pro with an update for better hardware acceleration.
If you have built a Plex server, pair it with Ryzen but ensure Intel drivers for Quick Sync. A common mistake is ignoring driver updates, which can lead to choppy streams.
Check if Fortnite is CPU or GPU intensive to optimize your gaming setup.
Latest Trends in Intel GPU Drivers:
In 2026, Intel GPU drivers focus on AI-based optimizations, better ray tracing on Arc GPUs, and improved stability. Features like XeSS upscaling now deliver better image quality with less performance loss.
Intel has also introduced legacy driver branches, where older CPUs receive security and stability updates but no new features.
Newer drivers are more tightly integrated with Windows 11 and DirectX 12, reducing crashes after OS updates and improving gaming and creative workloads.
Advanced Tips for Power Users:
For those diving deeper:
- Custom configurations: Edit registry for overclocking (risky backup first).
- Dual GPU setups: Use PRIME for Linux to switch between Intel and discrete cards.
- Monitoring tools: Install GPU-Z to track usage and temps in real-time.
- Scripting updates: Automate with PowerShell scripts for fleet management.
- Beta testing: Join Intel’s beta program for early access, but expect instability.
One common mistake? Overlooking BIOS updates, they unlock full GPU potential.
Explore how to undervolt CPU or GPU safely for better performance and lower temperatures
FAQs:
1. Do I need Intel GPU drivers if I have a dedicated GPU?
Yes, integrated graphics still handles video decoding and power efficiency tasks.
2. Are Intel GPU drivers safe to update?
Yes, when downloaded from Intel’s official site.
3. Can outdated Intel drivers cause crashes?
Absolutely, especially after Windows updates.
4. Should I use beta Intel GPU drivers?
Only for testing; WHQL drivers are safer.
5. Can Windows Update replace Intel GPU drivers?
Windows Update may install basic drivers, but Intel’s official drivers offer better performance and stability.
For external resources, visit Intel’s official support or Microsoft’s driver guide.
Conclusion:
Intel GPU drivers directly impact performance, stability, and compatibility. Using the correct driver, installing it cleanly, and knowing when to roll back prevent most graphics issues. For best results, prioritize Intel’s official drivers, update intentionally, and avoid unnecessary changes.
Image Disclaimer:
Some images used in this article, including the featured image, are screenshots from Intel Corporation’s and Microsoft Windows’ official software interfaces. These images are used strictly for educational and informational purposes under fair use.