What Does Overclocking a GPU Do? (The Ultimate Guide 2026)

Overclocking increases your GPU’s core and memory clock speeds beyond factory limits so it can process more calculations per second. The result is higher FPS in games, faster render times, and improved AI workload performance.
In 2026, with modern architectures like NVIDIA Blackwell and AMD RDNA4 already using aggressive boost algorithms, many users wonder: Is manual overclocking still worth it?
This guide explains how it works at a hardware level, real-world 2026 performance gains, safety limits, undervolting strategies, and when overclocking actually makes sense.
What Is GPU Overclocking?
GPU overclocking increases:
- Core clock: Controls shader and compute performance
- Memory clock: Improves VRAM bandwidth and texture performance
Modern GPUs already use dynamic boost algorithms. However, manual tuning lets you:
- Raise the power limit
- Adjust the voltage-frequency (V/F) curve
- Increase memory offset
- Optimize sustained boost behavior
Unlike beginner tutorials, proper overclocking focuses on sustained effective clocks, not just peak MHz.
Also Read: What Does Hardware Accelerated GPU Scheduling Do
Core vs Memory Clock (Real Impact)
Core Clock Impacts:
- FPS gains
- 1% low frame stability
- Ray tracing performance
- Compute workloads (Blender, AI inference)
Memory Clock Impacts:
- 4K/8K gaming
- High texture packs
- Ray tracing scenes
- Bandwidth-heavy AI workloads
In competitive 1080p gaming, core clock matters more.
In 4K ultra + ray tracing, memory scaling becomes critical.
Also Read: What Are ROPs in GPU?
How Modern Boost Algorithms Already Work?
Blackwell and RDNA4 GPUs dynamically boost until they hit:
- Power limits
- Thermal limits
- Voltage ceilings
Because of this, overclocking in 2026 is less about raw voltage and more about:
- Raising power headroom
- Improving cooling efficiency
- Optimizing the V/F curve
Stock tuning leaves less margin than older generations, but silicon variation still allows 8 to 15% gains on strong samples.
Also Read: Is Fortnite CPU or GPU Heavy?
How Does Overclocking a GPU Actually Work?
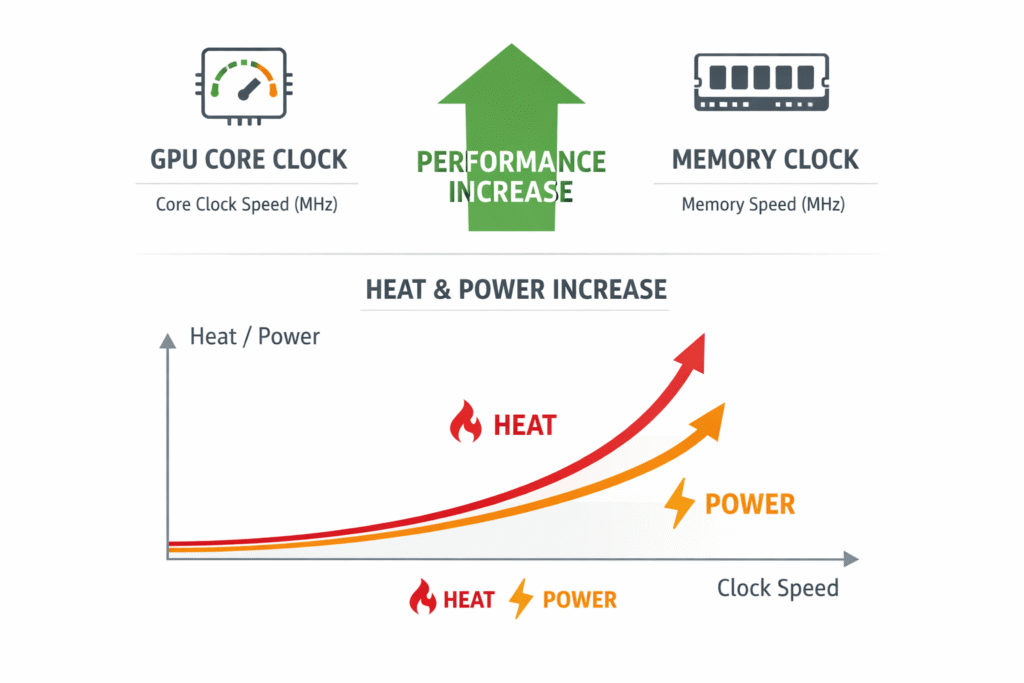
At the hardware level:
Higher clock speed = more instruction cycles per second.
That directly improves:
- Shader execution
- Texture mapping throughput
- ROP operations
- Frame time consistency
However, performance scaling is not linear. After a certain point, heat and power increase faster than FPS gains.
Key relationship:
Clock Speed ↑ → Performance ↑ → Heat ↑ → Power Draw ↑
Real 2026 Performance Gains:
Across modern AAA titles:
- 4K Ultra + RT: 7 to 12% average FPS gain
- 1440p competitive: 10 to 17% gain
- Blender Cycles: 10 to 16% faster renders
- Stable Diffusion & AI workloads: 8 to 14% higher throughput
The biggest improvement is often seen in 1% low FPS stability, not just average FPS, which directly improves perceived smoothness.
Risks & Real-World Tradeoffs
Heat & Power Draw
A high-end GPU can increase:
- +50 to 150 watts
- +8 to 15°C temperature
Without strong airflow, thermal throttling cancels out gains.
Long-Term Wear
Modern GPUs include:
- Thermal throttling
- Voltage caps
- Error correction in modern GDDR memory
Safe overclocking rarely shortens lifespan if voltage is controlled.
Damage usually comes from:
- Excessive voltage offsets
- Poor cooling
- BIOS flashing (not software tuning)
Is Overclocking Safe in 2026?
Yes, when done gradually and tested properly.
Built-in protections from manufacturers prevent catastrophic failure. Tools like MSI Afterburner and 3DMark make safe tuning accessible.
It is NOT recommended for:
- Thin laptops
- Poor airflow cases
- Stock blower coolers under heavy load
Best Tools for GPU Overclocking
- MSI Afterburner (manual control + profiles)
- NVIDIA App automatic tuning
- AMD Software: Adrenalin Edition
- OCCT for stability testing
For serious validation:
- Run at least 1 hour of real gameplay
- Monitor effective clock, not just peak boost
- Keep temperatures under 85°C sustained
For more detail to, visit this AMD Guide
Overclocking vs Undervolting (2026 Reality)
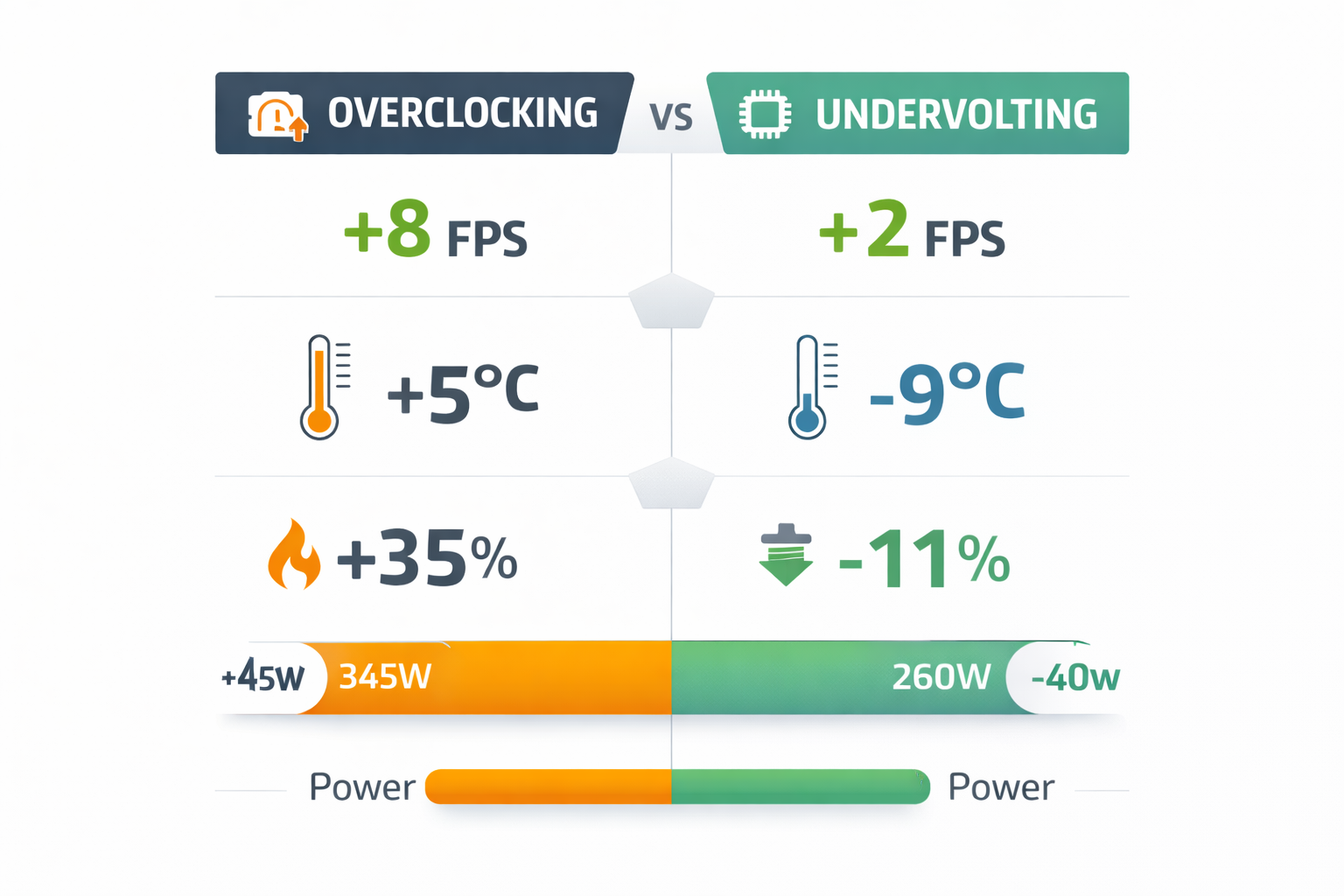
Many advanced users now combine both.
| Strategy | FPS Gain | Temps | Power Draw |
| Pure Overclock | +8 to 15% | Higher | Higher |
| Pure Undervolt | +0 to 5% | Lower | Lower |
| OC + UV Combo | +10 to 18% | Controlled | Moderate |
Undervolting improves efficiency and sustained clocks, often delivering better real-world performance than aggressive voltage increases.
Laptop GPU Overclocking
Possible, but limited.
Most laptops are:
- Power-limited
- Thermally constrained
Expected gains: 3 to 8% maximum
Better improvement strategy:
- Undervolt
- Repaste with high-quality thermal compound
- Improve airflow
Cost vs Performance in 2026
Spending $0 for 8 to 15% more performance is valuable.
However, if you need more than 15 to 20% uplift, upgrading to the next GPU tier is usually the smarter investment.
Overclocking is optimization, not a substitute for hardware scaling.
FAQ’s:
What does overclocking a GPU do?
It increases core and memory clock speeds, allowing the GPU to process more instructions per second, resulting in higher FPS and faster rendering.
Does overclocking increase FPS?
Yes, Real-world 2026 testing shows 7 to 17% FPS gains depending on resolution and cooling.
Is GPU overclocking safe?
Yes, if done gradually with temperature monitoring and stability testing.
Can overclocking damage a GPU?
Only if you push excessive voltage, ignore thermal limits, or skip stress testing.
How much should I overclock?
Start with +50 MHz core and +500 MHz memory, then increase gradually while testing stability.
Conclusion:
Overclocking a GPU in 2026 still delivers measurable performance gains, especially when combined with undervolting and proper cooling. While modern GPUs already boost aggressively, careful tuning can unlock 8 to 15% extra performance for free. The key is controlled power adjustments, temperature monitoring, and real-world stability testing.