CPU Fan Not Spinning – 2025 Expert Tips!

A CPU fan not spinning can happen due to a loose connection, dust buildup, or worn bearings. Ensure the fan is properly connected to the motherboard and clean any dust blocking the fan blades. If the issue persists, test the fan on another port. If that doesn’t work, check BIOS settings or replace the fan if the bearings are damaged.
Stay with us as we walk you through each problem step-by-step to keep your processor cool and your system running smoothly.
Why is My CPU Fan Not Spinning at All?
If your CPU fan is not spinning at all, the issue is often related to power or connection problems. Check for loose cables, a faulty fan motor, dust blocking the blades, or a dead CPU_FAN header. Reseating the fan connector, cleaning the fan, or testing it on a different header can help resolve the issue.
You may also like: Is 50°C Safe for CPU at Idle? – Expert Guide 2025!
How Do I Fix a CPU Fan That Suddenly Stopped Working?
1. Check Power Connections:
Make sure the fan is properly connected to the CPU_FAN header on the motherboard and the pins are seated correctly.
2. Inspect for Obstructions:
Check the blades for dust, debris, or anything that might be preventing movement.
3. Test on Another Header:
Plug the fan into another fan header. If it works there, the original header may be faulty.
4. Reset BIOS Settings:
Resetting the BIOS to default values often clears fan glitches or wrong fan profiles.
Why Does My CPU Fan Spin Sometimes and Stop Other Times?
A CPU fan that spins and stops repeatedly is usually caused by zero-RPM mode, which keeps the fan off at low temperatures. It can also happen due to worn bearings, weak voltage from the CPU_FAN header, or an overly low fan curve. Increasing the minimum fan speed in BIOS typically keeps the fan running consistently.
How Can I Check if My CPU Fan Header Is Faulty?

1. Swap Test:
Connect the CPU fan to another header. If it runs normally, the CPU_FAN header is likely damaged.
2. Voltage Check:
Use your BIOS to check the header’s voltage. If it’s unusually low or zero, the header may be faulty.
3. BIOS Monitoring:
If RPM shows on other headers but not on CPU_FAN, the tachometer signal isn’t being read correctly, which points to a failing header.
How Do I Know if My CPU Fan Is Getting Enough Power?
If the fan is not getting enough power, you may notice slow startup, inconsistent speeds, or the fan refusing to start altogether.
To confirm stable power:
- Make sure the connector is fully seated on CPU_FAN
- Check BIOS voltage and RPM readings
- Test the fan on another header and compare behavior
- Listen for weak or struggling startup sounds
You may also like: How to Check CPU Power Consumption? – Complete Guide 2025!
Why Is My CPU Fan Not Showing RPM in BIOS?
If your CPU fan is not showing RPM in BIOS, it’s usually due to a loose connector or a damaged tachometer (RPM) wire. Some fans also fail to report speed on certain motherboards. Reseating the cable, updating the BIOS, or restoring default settings typically fixes missing RPM readings and restores proper fan monitoring.
How Do I Fix CPU Fan Issues in BIOS Settings?
1. Check Fan Control Settings:
Make sure fan control is not disabled or limited by an overly low fan curve.
2. Restore Default Settings:
If the settings look incorrect, reset the BIOS to default.
3. Adjust Fan Curve:
Increase fan speed at lower temperatures to maintain consistent airflow.
What Should I Do if Dust Is Blocking My CPU Fan?
Dust can block airflow and prevent the blades from spinning freely.
- Turn off and unplug the PC
- Use compressed air to clean the blades and heatsink
- Hold the fan still while cleaning
- Clear any tough dust around the motor hub
- Manually spin the fan afterward to ensure smooth rotation
How Can I Test My CPU Fan on Another Header Safely?
SYS_FAN Header:
The SYS_FAN header provides safe, regulated power. If the fan spins when connected here, the CPU_FAN header may be faulty.
RPM Response:
If you see RPM and speed readings on the other header, it indicates that the fan is working properly.
Pump Headers:
Pump headers run at full speed, which can stress small CPU fans. Avoid using them for testing.
When Should I Replace a CPU Fan That Will Not Spin?
If your CPU fan will not spin after trying all troubleshooting steps, it’s time to consider replacing it. Signs that indicate a failing fan include:
- Motor Not Responding: If the motor does not react to power, it may be damaged beyond repair.
- Grinding, Rattling, or Wobbling: Unusual noises could indicate worn-out bearings or other mechanical issues.
- No Movement with Correct Voltage: If the fan does not spin even when the correct voltage is applied, it could be an issue with the motor or fan components.
In these cases, replacing the fan is the best option to ensure your system stays cool and operates efficiently.
Is It Safe to Use a PC When the CPU Fan is Not Spinning?
No, it is not safe to use a PC when the CPU fan is not spinning. Without active cooling, the CPU can overheat within seconds, leading to thermal throttling, crashes, sudden shutdowns, or even permanent hardware damage. Always ensure the CPU fan is running before using your system to prevent overheating.
How Do I Adjust Fan Curve Settings to Keep the Fan Spinning?
1. Enter BIOS:
Open your system’s BIOS/UEFI settings and navigate to the fan configuration menu.
2. Adjust Fan Curve:
Increase the minimum fan speed to ensure the fan starts spinning at lower temperatures and maintains a consistent speed.
3. Save and Exit BIOS:
Save the changes to apply the updated fan curve profile and exit BIOS.
What Causes a CPU Fan Motor or Bearing to Fail?
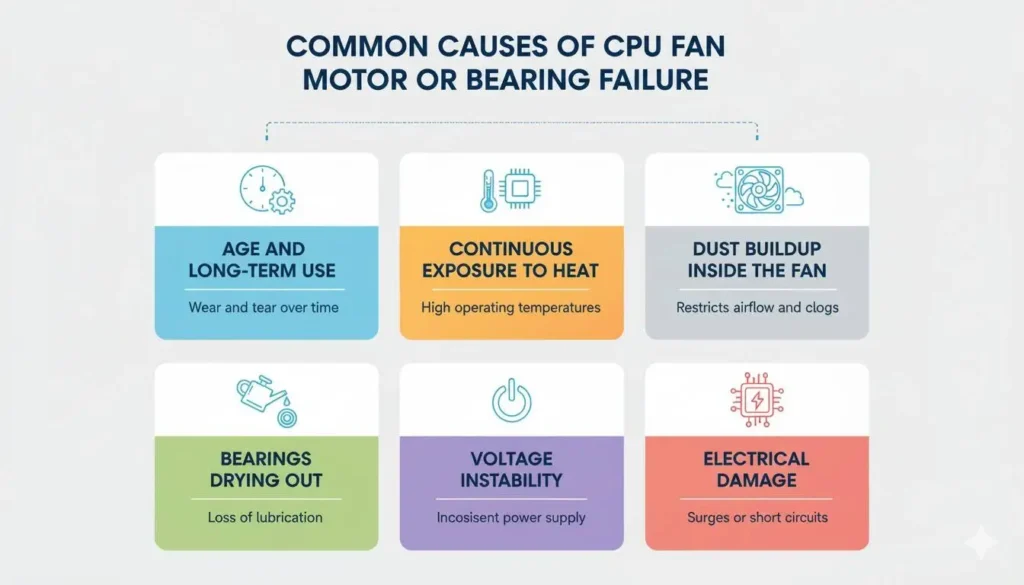
Fan motors and bearings naturally wear out over time.
Common causes include:
- Age and long-term use
- Continuous exposure to heat
- Dust buildup inside the fan
- Bearings drying out
- Voltage instability or electrical damage
Regular cleaning and timely replacement help maintain stable cooling performance.
FAQs:
1. Do CPU fans slow down with age?
Yes. Dust and worn bearings gradually reduce speed.
2. Can thermal paste problems affect the fan?
Not directly, but high temperatures from bad paste can force the fan to run harder.
3. Does a broken tachometer wire stop the RPM reading?
Yes, without this wire the motherboard cannot detect speed.
4. Can a motherboard update fix fan problems?
Sometimes. Firmware updates can fix RPM detection and fan control issues.
5. Should a CPU fan start immediately when the PC powers on?
Yes, unless the motherboard uses zero-RPM mode.
Conclusion:
A CPU fan not spinning is usually caused by loose cables, dust buildup, worn bearings, motor failure, or incorrect BIOS settings. Cleaning the fan, reseating the connector, testing the CPU_FAN header, and adjusting the fan curve often fix the issue. If nothing works, replacing the fan ensures proper airflow and protects your PC from overheating.