How to Check Motherboard Damage From GPU – Signs, Testing Steps & Fixes!

A damaged GPU can harm the motherboard by overloading power circuits or shorting PCIe lanes. To check for damage, inspect the PCIe slot for burns or bent pins, test the system with another GPU, and run motherboard diagnostics. If the PC only fails with the old GPU installed, the motherboard is likely affected.
This guide walks you through every sign, testing method, and fix so you can confirm issues accurately and protect your hardware.
How a GPU Can Damage a Motherboard:
Many users think a GPU can not damage a motherboard, but certain failures can still cause harm. Power surges, faulty PCIe connections, or short circuits may create serious issues. Understanding these risks helps you accurately check motherboard damage from GPU during troubleshooting.
Power delivery conflict:
A damaged GPU VRM or shorted capacitor can send abnormal power draw through the PCIe slot, stressing the motherboard’s power circuitry.
PCIe slot overload:
A GPU that overheats or experiences a hard short can cause the PCIe slot to burn, melt, or develop carbon marks.
Faulty PSU interaction:
If the PSU sends unstable voltage to the GPU, the GPU may pass irregular current back into the motherboard traces.
Signs Your Motherboard Might Be Damaged:
Before opening the PC, you should understand the most common symptoms that indicate motherboard damage caused by the GPU.
System not posting:
If the PC turns on but shows no display, the GPU or the PCIe slot may be damaged.
Long or repeating beeps:
Most motherboards release beep codes when components fail. Continuous beeps often indicate GPU or PCIe failures.
Burnt smell or visible marks:
Burn spots, discoloration, or melted plastic near the PCIe slot are strong signs of electrical damage.
Visual Inspection Steps for PCIe Slot Damage:
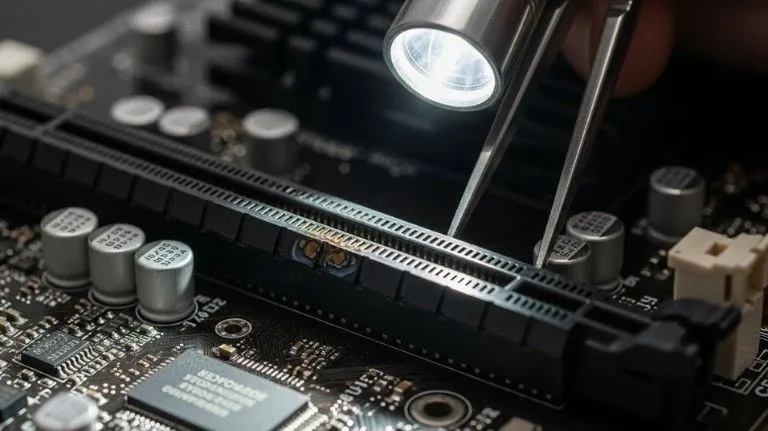
A careful visual inspection is one of the fastest and safest ways to detect GPU-caused motherboard damage. Always turn off the PC, remove the power cable, and ground yourself before starting.
Step-by-step procedure:
- Remove the GPU from the PCIe slot using the rear bracket screws.
- Look directly into the PCIe slot using a flashlight.
- Check the contacts for discoloration, bent pins, or burn marks.
- Inspect surrounding capacitors for bulging or leaking.
- Check the motherboard PCB layers for cracks or lifted traces.
What damage looks like:
Burn marks, dark residue, melted plastic, or warped materials often indicate that the GPU transferred excessive current or shorted out the PCIe port.
How to Test the PCIe Slot for Proper Function:
After visual inspection, perform functional testing to confirm that the motherboard’s PCIe slot still functions correctly. For official PCIe specifications and slot guidelines, visit the PCI-SIG official website.
Use a known-good GPU:
Insert another functional GPU to check if the system boots normally.
Use a secondary PCIe slot:
If the motherboard has multiple PCIe slots, test the GPU in a different slot to identify whether the first slot is faulty.
Boot without a GPU:
If your CPU includes integrated graphics (Intel iGPU or AMD APU), remove the GPU and connect the monitor directly to the motherboard’s HDMI or DisplayPort port.
Power Delivery Problems Caused by Bad GPUs:
Power delivery problems from a bad GPU can harm the motherboard if voltage spikes or rail overloads occur. A failing GPU can stress the PSU’s 12V rail, while loose or burnt PCIe connectors can send unstable power into the PCIe slot. These issues make it important to check motherboard damage from GPU when diagnosing hardware failures.
Related Guide: CPU Over Voltage Error – Causes, Solutions & Prevention!
How to Check for Burnt Components on the Motherboard:
In many cases, burnt components are small and difficult to see. You should carefully inspect the power phases and capacitors around the PCIe slot.
Components to check:
- MOSFETs around the GPU PCIe area
- Capacitors near the first PCIe slot
- Inductors and coils that handle power regulation
- VRM components near the CPU area that may also be affected
What damaged parts look like:
Cracks, leaking electrolyte, bulges, and blackened areas indicate electrical failure.
Also Read: CPU Over Temperature Error – Causes and Solutions 2025!
Testing With Another GPU or Integrated Graphics:
To confirm whether your original GPU caused the issue, test with a different working graphics card or rely on integrated graphics if available.
When another GPU works:
If another GPU works in the same slot, your motherboard is fine and the problem is with the original GPU.
When nothing works at all:
If no GPU works and integrated graphics fail to boot, the motherboard likely has deeper power or PCIe lane damage.
BIOS and Diagnostic Tool Checks:
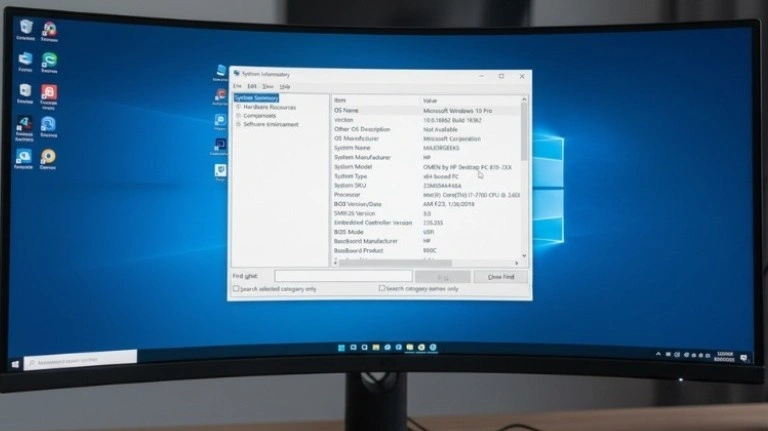
Sometimes motherboard damage can appear in BIOS readings or system diagnostics. This makes software testing useful after a basic inspection.
What to check in BIOS:
- PCIe link speed (x16, x8, x4, x1)
- GPU detection status
- Voltage readings
- System event logs
Diagnostic tools:
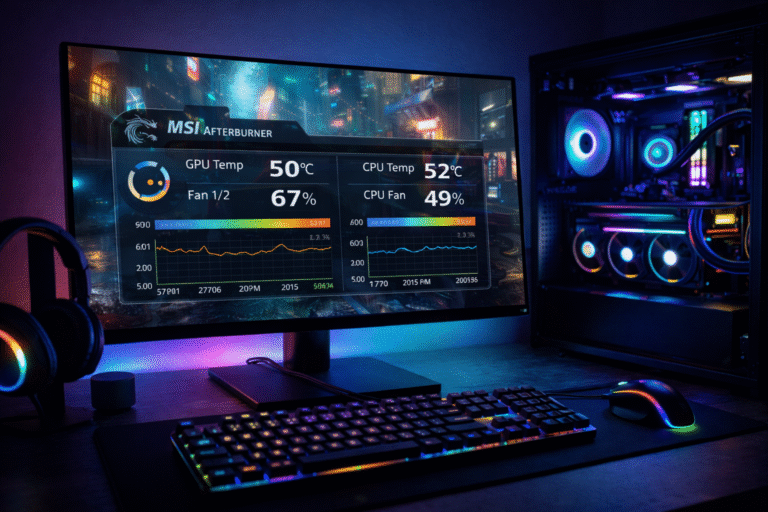
Use tools like HWInfo, GPU-Z, and motherboard manufacturer utilities to detect unusual GPU behavior.
Troubleshooting No-Display and Boot Issues:
No display issues can occur because of many reasons, and not all of them indicate motherboard damage. Follow a layered approach to confirm the problem.
Quick troubleshooting list:
- Re-seat the GPU
- Check the display cable and port
- Clean the PCIe slot with compressed air
- Reset CMOS
- Test RAM and PSU
If the GPU still does not show any signal, the motherboard’s PCIe controller may be damaged.
You May Like: CPU Fan Error on Boot – Fix It Now 2025!
Can a Faulty GPU Permanently Damage a Motherboard?
This is one of the most common PAA questions. The short answer is yes, but it is relatively rare.
When permanent damage occurs:
Permanent damage typically happens only when:
- The GPU shorts internally
- The PSU is low-quality or unstable
- The PCIe slot overheats or melts
- The GPU VRM burns through the PCIe traces
- There is a sudden surge or electrical fault
Tips to Avoid GPU Causing Motherboard Damage:
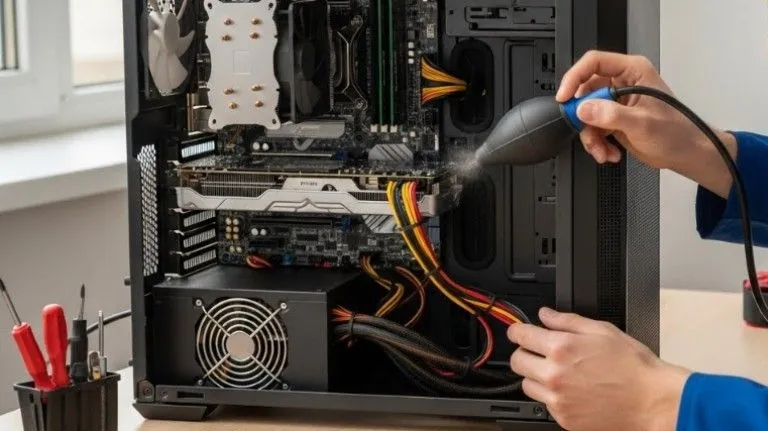

Even if your motherboard is working, prevention ensures no future problems occur.
What you should always do:
- Use a high-quality PSU with proper wattage
- Regularly clean dust from the GPU and PCIe slot
- Check PCIe cables for tight connections
- Avoid overclocking on unstable hardware
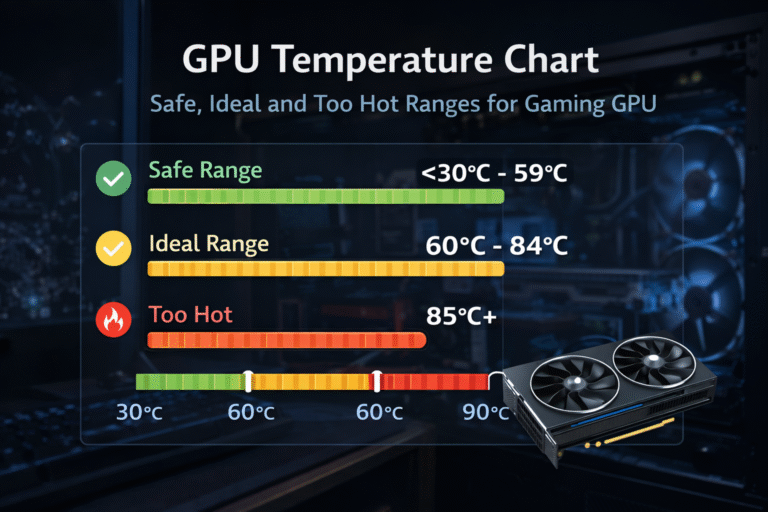
- Monitor GPU temperatures for abnormal spikes
- Replace cheap riser cables if using an open case or mining setup
When to Replace the Motherboard or GPU?:
There are clear situations where replacement is better than repairing. Because motherboard repair is complex, most users choose replacement.
Replace the motherboard if:
- PCIe slot is burned or melted
- System does not detect any GPU
- Visible PCB damage exists
- Power phases are cracked or leaking
Replace the GPU if:
- GPU causes crashes on multiple systems
- Fans or VRAM are overheating
- GPU does not display anything, even in a working motherboard
- PCIe connectors are burnt or broken
Conclusion:
Checking for motherboard damage from a GPU starts with simple visual and performance tests. Look for burns, bent pins, or no-display issues, then swap in another GPU to check motherboard damage from GPU properly. If the issues stay, the motherboard may be failing. Good cooling and a quality PSU help prevent future problems.
FAQs:
1. Can a GPU damage the PCIe slot?
Yes, if the GPU shorts, overheats, or draws abnormal power, it can burn or melt the PCIe slot.
2. What are the signs of a damaged motherboard from a GPU?
Burn marks, no display, beep codes, crashing under load, and failure to detect the GPU.
3. Can a motherboard be repaired if the PCIe slot is burnt?
Technically, yes, but repairs are expensive and often unreliable. Replacement is recommended.
4. Does a faulty PSU increase the chances of GPU damaging the motherboard?
Yes. An unstable or low-quality PSU can send irregular voltage to the GPU, which may flow into the motherboard.
5. How do I know if my GPU is dead or if the motherboard is damaged?
Test the GPU on another system or test another GPU on your motherboard. This immediately reveals the faulty part.