What Is A GPU? (Ultimate Guide 2026)

A GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) is a computer component designed to process images, videos, and graphics at very high speed. Unlike a CPU, which processes tasks sequentially, a GPU can perform thousands of tasks simultaneously. This makes it essential for gaming, video editing, 3D rendering, and modern AI applications.
In this guide, we will clearly explain what a GPU is, how it works, and why it matters so you can choose the right hardware for performance-focused tasks and everyday computing.
What Is a GPU and What Does It Do?
A GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) is a specialized processor responsible for handling visual output. It ensures that images, videos, games, and animations appear smooth and clear on your screen.
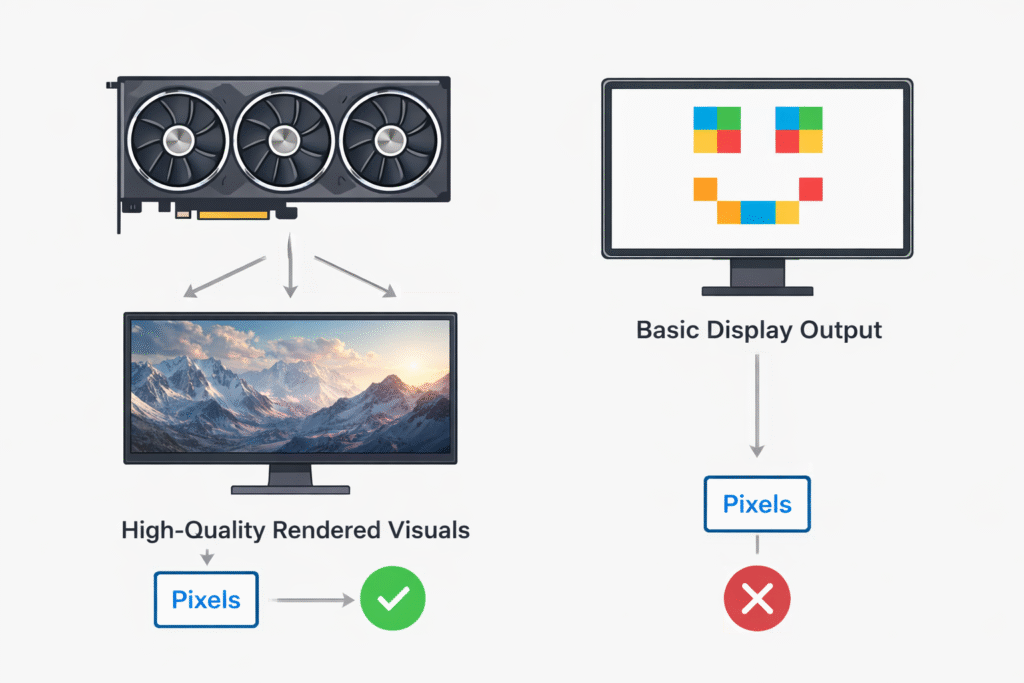
A GPU:
- Processes millions of pixels at the same time
- Reduces workload on the CPU
- Improves visual quality and system responsiveness
Without a GPU, modern applications and graphics-heavy software would run slowly and inefficiently.
Why Is a GPU Important in Modern Computing?
Today’s software relies heavily on graphics and parallel processing. From gaming and video streaming to AI-powered tools and web browsers, GPUs play a critical role.
GPUs:
- Improve overall system speed and performance
- Handle complex visual and computational tasks efficiently
- Enable multitasking and smooth user experiences
This is why even basic systems now include some form of GPU.
How Does a GPU Work?
A GPU works by dividing large tasks into thousands of smaller ones and processing them simultaneously. This approach is called parallel processing.
Key working principles:
- Uses thousands of small processing cores
- Performs calculations in parallel instead of sequentially
- Renders images frame by frame for smooth visuals
This design makes GPUs extremely powerful for graphics and data-heavy workloads.
Also Read: GPU Fans Not Spinning?
What Is the Difference Between a GPU and a CPU?
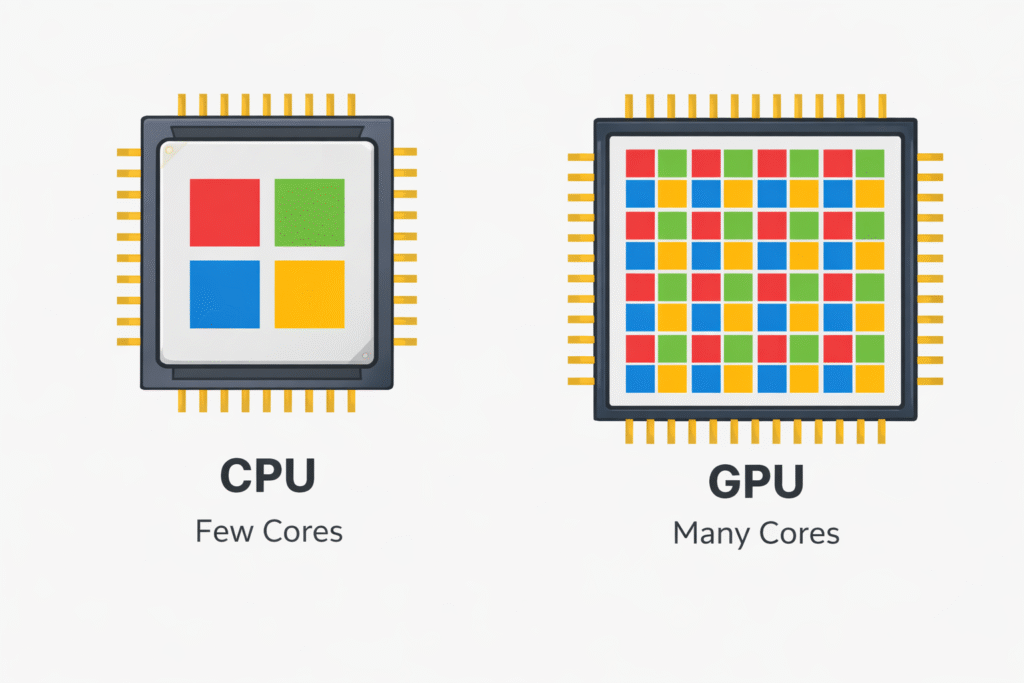
The CPU and GPU serve different purposes but work together to deliver performance.
| Feature | CPU | GPU |
| Main Job | General computing tasks | Graphics and parallel processing |
| Cores | Few powerful cores | Thousands of smaller cores |
| Best For | Logic, control, multitasking | Gaming, AI, rendering |
Simply put, the CPU is the system’s brain, while the GPU is its visual and processing engine.
What Are the Different Types of GPUs?
GPUs come in different forms depending on user needs.
- Integrated GPU: Built into the CPU; suitable for browsing, office work, and media playback
- Dedicated GPU: A separate graphics card offering high performance for gaming and editing
- Workstation GPU: Designed for professional tasks like 3D modeling, CAD, and simulations
Choosing the right type depends on how demanding your workload is.
What Is a GPU Used For?
Modern GPUs are used far beyond gaming. Their parallel processing power supports many technologies.
Common uses include:
- Gaming and high-end graphics rendering
- Video editing, animation, and content creation
- Artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analysis
GPUs have become a core component of modern computing systems.
Which GPU Is Best for Gaming, Editing, or AI?
There is no single best GPU for everyone. The right choice depends on your use case.
| Use Case | Recommended GPU Type |
| Gaming | NVIDIA RTX or AMD RX series |
| Video Editing | RTX GPUs with higher VRAM |
| AI & Machine Learning | NVIDIA GPUs with CUDA support |
Always balance performance, budget, and future needs when choosing a GPU.
Also Read: How to Check GPU Health
What Factors Affect GPU Performance?
Several hardware and software elements influence GPU performance.
Important factors include:
- GPU architecture and core speed
- VRAM size and memory type
- Cooling solution and power supply support
A powerful GPU performs best when paired with proper cooling and a compatible system.
Also Read: What Temp Should My GPU Be?
How Much VRAM Do You Need in a GPU?
VRAM (Video Random Access Memory) stores textures and graphical data. Insufficient VRAM can limit performance.
| Usage | Recommended VRAM |
| Daily Tasks | 2 to 4 GB |
| Gaming | 6 to 8 GB |
| Editing & AI | 10 to 24 GB |
Higher resolutions and professional workloads benefit from more VRAM.
Is a Dedicated GPU Necessary for Everyday Use?
For basic tasks like browsing, streaming, and office work, a dedicated GPU is not required.
- Integrated GPUs handle daily use efficiently
- They consume less power and reduce system cost
- Dedicated GPUs are only necessary for heavy workloads
Casual users can comfortably rely on integrated graphics.
What Is the Future of GPUs?
GPUs are evolving rapidly and will remain essential in future technology.
Expected developments include:
- Stronger AI and machine learning acceleration
- Improved performance per watt
- Wider use in autonomous vehicles and smart systems
GPUs will continue shaping the future of computing and automation.
FAQs:
What is a GPU used for besides gaming?
GPUs are widely used in video editing, 3D rendering, AI training, data analysis, and scientific simulations.
Is a GPU necessary for everyday computing?
No. Integrated GPUs are sufficient for basic tasks. Dedicated GPUs are only needed for demanding workloads.
How does a GPU improve performance?
A GPU handles parallel tasks efficiently, reducing processing time for graphics and computations.
Can a GPU replace a CPU?
No. CPUs and GPUs have different roles and work best together.
How much VRAM do I need?
It depends on usage. Higher resolutions and professional tasks require more VRAM.
Conclusion:
Understanding what a GPU is has become essential in today’s performance-driven computing world. GPUs have evolved far beyond basic graphics processing and now power gaming, creative workflows, and advanced research.
By learning how GPUs work, their types, and how to choose the right one, users can make smarter hardware decisions. As technology advances, GPUs will continue to play a central role in the future of computing.