What Temp Is Too Hot for CPU? – Keep It Cool!

A CPU temperature above 85°C is usually considered unsafe for most processors. Short spikes during gaming or heavy workloads are normal, but if a CPU stays too hot for too long, it can cause thermal throttling, performance drops, and long-term hardware damage. In general, the safe CPU temperature range for daily use is between 60°C and 75°C.
Many users also ask what temperature should a CPU not exceed, especially when monitoring temps for the first time. In this 2025 expert guide, we explain normal CPU temperature ranges, warning signs of overheating, and practical cooling tips to keep your system stable, efficient, and protected over the long term.
How Do You Check and Understand CPU Temperature Readings?
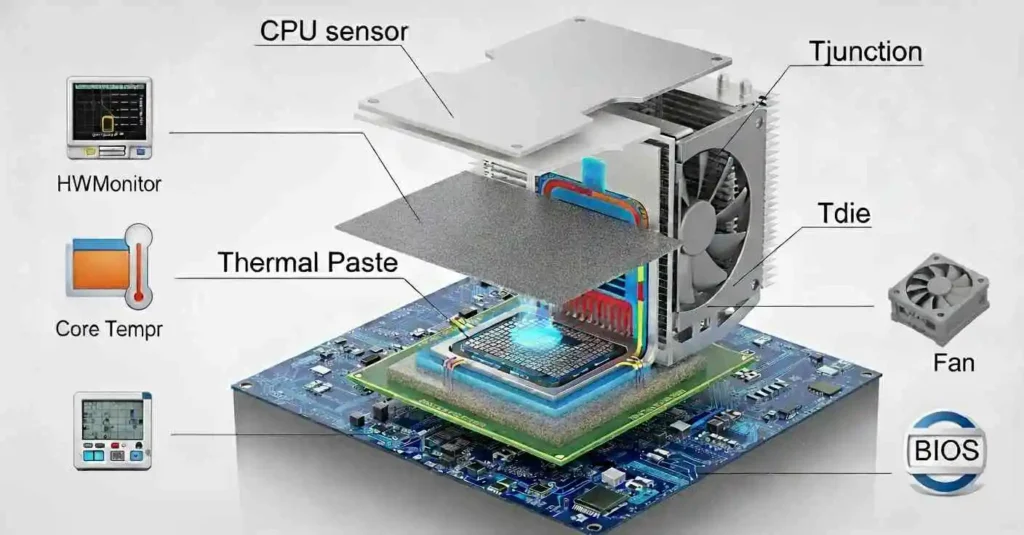
CPU temperature shows how much heat your processor creates while it works. It is measured using built-in sensors inside the chip that track heat levels in real time. You can view these readings in °C using simple monitoring tools.
How CPU Temperature Is Measured:
- Tjunction (Junction Temperature): Maximum safe temperature limit before the CPU starts throttling, usually around 100°C.
- Tdie (Die Temperature): Shows the real-time internal temperature directly from the CPU core or die.
- Monitoring Tools: Software like HWMonitor, Core Temp, or HWiNFO displays live temperature readings for each core.
- BIOS or UEFI: You can also check CPU temperature directly from the BIOS/UEFI menu before the OS loads.
Now that you know how CPU temperature is measured, let’s look at why processors generate heat in the first place.
Why Do CPUs Produce Heat?
CPUs produce heat because electrical energy turns into thermal energy during processing. As the processor works harder, it draws more power, creating more heat. Without proper cooling, this buildup can quickly reach levels where the temp is too hot for CPU stability and performance.
Main Reasons:
- Higher voltage and clock speeds increase power use.
- More cores and heavier workloads increase thermal output.
- Poor airflow or cooling traps heat inside the system.
- Background tasks and overclocking push temperatures even higher.
Understanding what causes heat makes it easier to see what temperatures are considered safe for your CPU.
What Are the CPU Temperature Thresholds for Intel and AMD?
CPU temperature limits vary by processor brand and design. Intel CPUs usually prefer slightly lower temperatures, while AMD Ryzen processors are built to handle higher heat under load.
Many users worry when temperatures reach around 80°C, but this is not always unsafe. For modern CPUs, especially Ryzen chips, this can still be normal depending on cooling and airflow. If you are unsure, read Is 80°C hot for a CPU and understand when heat actually becomes a problem.
Keeping your CPU near its maximum temperature for long periods can still reduce performance, so proper cooling and airflow are always recommended.
| CPU Model | Idle Temps (°C) | Normal Load (°C) | Max Safe Temp (°C) | Throttling Point (°C) |
| Intel Core i9-13900K | 35-45 | 60-70 | 100 | 95 |
| Intel Core i7-12700K | 30-40 | 55-65 | 100 | 90 |
| Intel Core i5-11600K | 30-40 | 50-65 | 95 | 85 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 7950X | 40-50 | 65-75 | 95 | 90 |
| AMD Ryzen 7 5800X | 35-45 | 60-70 | 90 | 85 |
| AMD Ryzen 5 5600X | 35-45 | 55-65 | 90 | 80 |
CPU temperature limits depend on each processor’s design. Intel and AMD CPUs manage heat differently, resulting in unique safe operating ranges. The table below compares popular models and their maximum safe temperatures.
When Does a CPU Start Overheating?
CPU overheating occurs when temperatures remain above 85°C to 90°C for extended periods, causing throttling and performance drops. At this point, performance drops as the system triggers thermal throttling to prevent damage.
Common Signs of Overheating:
- Constant high fan noise.
- Sudden system slowdowns or freezes.
- Automatic shutdowns under load.
- Temperature spikes even during light use.
Once you know the signs of overheating, it is useful to compare how CPU temperatures behave at idle versus heavy load.
At idle, CPUs usually run much cooler, and if you are wondering whether 50°C is safe for a CPU at idle, it is generally acceptable for short periods, depending on airflow and room temperature.
What Causes Sudden CPU Temperature Spikes?
Sudden CPU temperature spikes can make users wonder what temp is too hot for CPU performance. These jumps often occur when background apps start running, turbo boost activates, or voltage changes suddenly. Poor airflow or old thermal paste can also cause quick rises in heat even during light workloads.
Is It Normal for CPU Temperature to Fluctuate?
Yes, small CPU temperature changes of 5°C–15°C are completely normal as workloads and fan speeds vary. However, if temperatures keep spiking or stay too high above 85°C, it may indicate poor cooling, dust buildup, or unstable voltage settings.
What Are the Signs of an Overheating CPU?
An overheating CPU shows clear warning signs, such as sudden slowdowns, random shutdowns, and loud fan noise. Ignoring these signs can damage your processor over time.
Main Signs of Overheating:
- Sudden frame drops or lag during gaming.
- Frequent system crashes or restarts.
- Fans are running at full speed constantly.
- CPU temperature stays above 85°C even at light load.
- Unusual smell or heat from the PC case.
Does High CPU Temperature Shorten CPU Lifespan?
Yes, high temperatures can damage a CPU over time. Too much heat harms its parts, slows performance, and shortens its lifespan.
Short-Term Effects:
- Thermal throttling lowers performance to control heat.
- System instability or unexpected shutdowns.
Long-Term Effects:
- Gradual wear on transistors and circuits.
- Permanent reduction in CPU efficiency.
- Higher risk of complete processor failure.
Why Is My CPU Hot Even With a Good Cooler?
A CPU can still run hot even with a good cooler if airflow, thermal paste quality, or voltage settings are not optimized. Dust buildup or poor case ventilation can also trap heat. Sometimes, the temp is too hot for a CPU simply because the system’s airflow balance is not effective enough.
Common Reasons:
- Poor case airflow or blocked vents.
- High ambient (room) temperature.
- Incorrect cooler installation or low-quality thermal paste.
- Overvolting or aggressive boost settings.
- Dust buildup on fans or radiator fins.
In short, even a good cooler cannot help if the airflow, voltage, or paste quality is not proper. Regular cleaning and balanced ventilation are key to preventing overheating and ensuring long-term, stable performance.
Also Read: How to Check RAM Clearance Before Installing a CPU Cooler (2025)
Does Room Temperature Affect CPU Heat?
Yes, room temperature directly affects CPU heat. A warmer environment makes it harder for your cooling system to push out hot air, raising the CPU’s overall temperature.
Key Points:
- Higher ambient temperatures reduce cooling efficiency.
- A 5°C increase in room temperature can raise CPU temperatures by 3–5°C.
- Proper ventilation and cool airflow in the room help maintain stable CPU performance.
Do BIOS or Voltage Settings Raise CPU Temps?

Yes, BIOS and voltage settings can raise CPU temperatures if not correctly configured. Overvolting or enabling performance boost options often increases heat output.
Voltage Settings:
- Higher voltage means more power draw and extra heat.
- Undervolting helps reduce temps without losing performance.
BIOS Configuration:
- Auto-boost or Turbo modes push the CPU to higher limits.
- An outdated BIOS can mismanage fan curves or voltage levels.
Improve Case Airflow:
- Use balanced intake and exhaust fans for steady air movement.
- Avoid blocking vents or placing the PC near walls.
Maintain the Cooling System:
- Clean dust from fans and radiators every few weeks.
- Replace old thermal paste for better heat transfer.
Adjust Power and BIOS Settings:
- Lower the voltage slightly to reduce the power draw.
- Set fan curves in BIOS for optimal cooling response.
Keep the Environment Cool:
- Keep your PC in a well-ventilated, cool area.
- Avoid direct sunlight or enclosed spaces that trap heat.
How to Balance CPU Performance and Heat?
Balancing CPU performance and heat means finding the right mix of speed and temperature. A few smart settings can keep your system fast without overheating.
Optimize Power Settings:
- Use Windows “Balanced” mode for efficient power use.
- Avoid running at maximum performance all the time.
Control Voltage and Clock Speeds:
- Slight undervolting helps cut heat with little to no speed loss.
- Moderate clock speeds prevent thermal buildup during heavy loads.
Upgrade and Maintain Cooling:
- Keep coolers, fans, and airflow in top condition.
- Consider an AIO or better thermal paste for lasting results.
Monitor Regularly:
- Use tools like HWMonitor or Core Temp to track heat changes.
- Adjust settings when temps consistently exceed safe limits.
FAQ’s:
1. How often should I check my CPU temperature?
It is good to check once a week or after installing new hardware, gaming, or heavy rendering sessions.
2. Can dust alone make my CPU overheat?
Yes, dust buildup blocks airflow and traps heat, raising CPU temps by several degrees.
3. Does undervolting really help reduce CPU heat?
Yes, undervolting lowers power draw, which cuts down heat without hurting performance.
4. Can background apps cause high CPU temperature?
Absolutely. Unnecessary background processes increase CPU load, which raises the temperature even when idle.
5. How do I know if my CPU cooler is failing?
If you hear unusual noises, notice temperature spikes, or experience slower performance, your cooler might need cleaning or replacement.
Conclusion:
When the temp is too hot for CPU, it can cause slow performance, random crashes, or even permanent damage over time. Keeping your processor within safe temperature limits ensures stable, long-lasting performance. Use this 2025 CPU temperature guide to maintain ideal temps and prevent overheating issues.