Why Are My GPU Fans Not Spinning? (Zero RPM, Software & Hardware Fixes)

If your GPU fans are not spinning, don’t panic. In many cases, it’s completely normal. Modern graphics cards use Zero RPM mode, where fans stay off until temperatures reach around 50–60°C. However, if the fans remain inactive even under heavy load, it may point to driver issues, software glitches, loose fan connections, or failing hardware.
In this guide, we will walk through clear diagnostics and practical fixes to get your GPU cooling properly again before heat becomes a serious problem.
Is It Normal for GPU Fans not to Spin?
Modern GPUs are smart about cooling. Fans often sit idle when your card’s not working hard, saving energy and cutting noise. Think of it like a car engine it doesn’t rev at a stoplight. But if fans ignore high temps or heavy tasks, that’s a red flag.
In real-world setups, I have seen users panic over silent fans during boot-up, only to find it’s by design. For beginners, this means no worry if temps stay low. Advanced folks might tweak this for constant airflow.
Normal: Fans off below 50°C, spinning up during games. Abnormal: No spin at 80°C+, risking damage. Always monitor to catch issues early.
Common Reasons Why GPU Fans Stop Spinning:
- Zero RPM Mode: Many cards from NVIDIA and AMD keep fans off until needed, a feature called Zero Frozr on MSI models or similar in others.
- Software Glitches: Outdated drivers or conflicting apps like overlays can mess with fan controls.
- Hardware Problems: Loose power cables, dust buildup, or worn bearings might halt spins.
- Temperature Sensors: Faulty sensors fool the GPU into thinking it’s cool when it’s not.
- Power Supply Issues: Insufficient wattage or faulty PSU rails fail to power fans properly.
These causes overlap sometimes. For instance, a dusty card might overheat without fans reacting, mimicking a sensor fault.
If you have built PCs before, you know dust is a serious problem , it insulates like a blanket, raising temps quietly.
Is Zero RPM Mode Normal or a Problem for GPUs?
Zero RPM mode prioritizes silence, turning fans on only above thresholds like 55°C for NVIDIA or adjustable in AMD software. It’s great for quiet offices but tricky in hot climates.
Boot a demanding game and watch temps climb. If fans kick in around 60°C, it’s normal. If not, disable the mode.
Beginners love this for noise reduction, but advanced users often override it for longevity. In my experience, leaving it on is fine unless you are overclocking.
Tip: Ever notice your PC whisper-quiet during emails? That’s zero RPM at work, but don’t ignore it during renders.
How to Check If Your GPU Is Overheating (For Beginners):
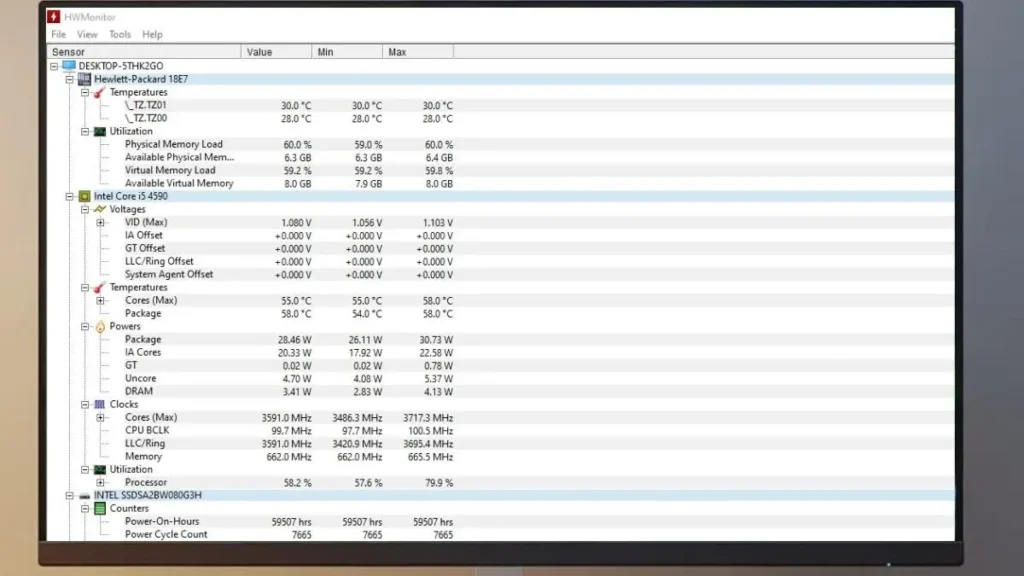
Overheating sneaks up if fans fail. Use tools to spot it early.
First, download free monitors like HWMonitor or GPU-Z. They show real-time temps, usage, and fan speeds. Idle temps under 50°C, load temps below 85°C for most cards. If higher without fans spinning, act fast.
A quick scan during stress tests can reveal overheating patterns early and help prevent crashes.
For advanced checks, log data over sessions to graph trends useful for spotting intermittent issues.
How to Fix GPU Fans Not Spinning Using Software:
Fan curves dictate when and how fast fans spin based on temps. Default ones might be too lax.
NVIDIA: Use the NVIDIA App or GeForce Experience to tweak. Set fans to start at 40% speed from 50°C, ramping to 100% at 80°C.
AMD users: In Radeon Software’s Adrenaline, go to Performance > Tuning > Fan Tuning. Toggle zero RPM off and customize.
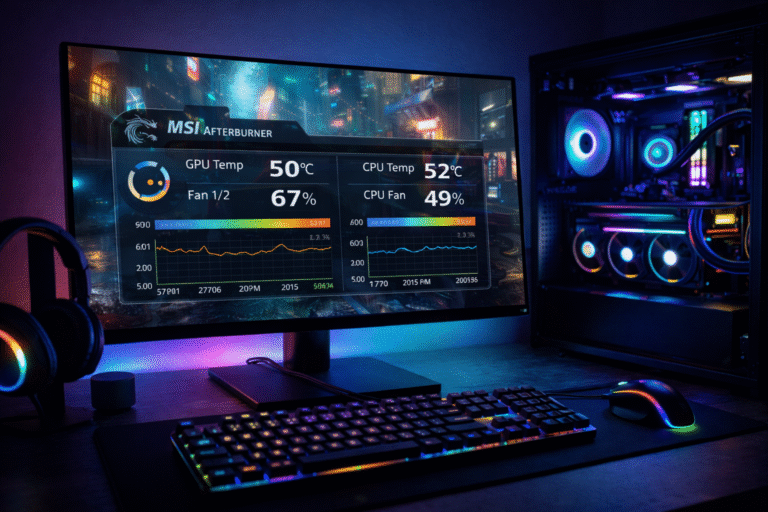
Third-party tool: MSI Afterburner works for both, letting you draw curves manually.
Start conservatively to avoid noise. One common mistake? Forgetting to apply changes always test post-tweak.
This approach bridges beginner ease with advanced control, like fine-tuning for specific games.
For more on GPU health monitoring, see our How to Check GPU Health – Simple & Expert Guide.
Hardware Checks: Power Cables and Fan Connections
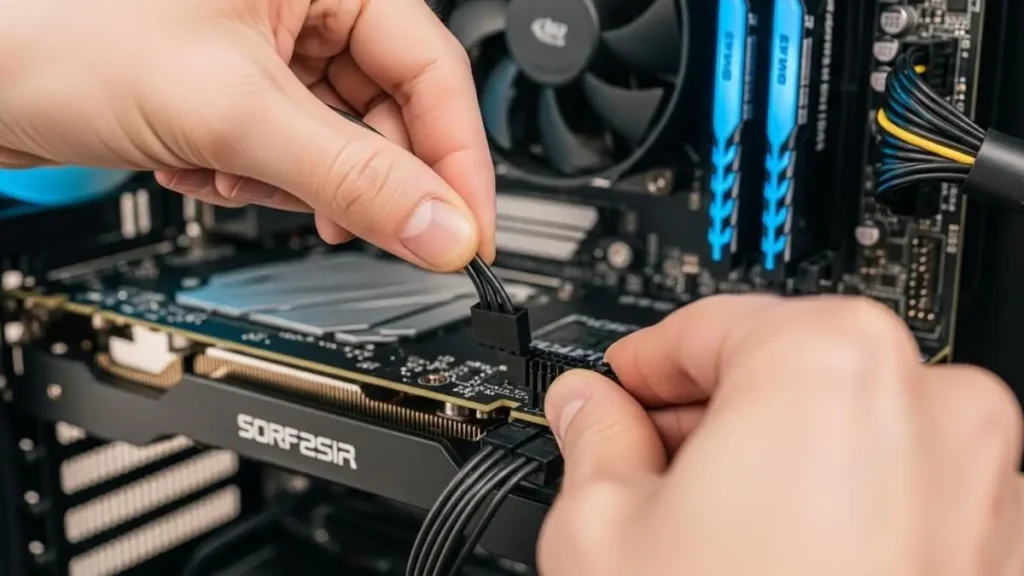

Sometimes it’s physical. Unplug and reseat your GPU’s power cables those 6-pin or 8-pin connectors must click firmly.
Inspect for damage: Bent pins or frayed wires spell trouble. Clean dust from fans with compressed air, gently.
Check PSU: Ensure it’s rated high enough, say 650W+ for mid-range cards. Test with a spare if possible.
In some cases, limited space inside the PC can pull on cables, and adjusting them can fix fan issues.
Tip: Use a multimeter to verify voltage on rails is steady at 12V.
How to Troubleshoot GPU Fan Problems:
- Monitor Basics: Install HWInfo or similar, run a benchmark like FurMark, and note temps and fan RPM.
- Software Reset: Uninstall drivers with DDU in safe mode, reinstall latest from NVIDIA or AMD sites.
- Disable Zero RPM: In GPU software, turn off silent modes and set manual fan speed to 50% to test spin.
- Hardware Inspection: Power off, reseat GPU in PCIe slot, check all cables, and clean dust.
- Stress Test: Run games or Unigine Heaven; if fans don’t spin at 70°C+, proceed to advanced.
- BIOS Check: Enter UEFI, ensure PCIe settings are auto, update BIOS if outdated.
- Alternative Slot/PSU: Try another PCIe slot or PSU to isolate issues.
- Fan Control Apps: Use Afterburner to force spin; if it fails, suspect a hardware fault.
Follow sequentially. Most issues are resolved by step 4.
Advanced GPU Fan Testing Tools and Methods:
Dive deeper with specialized tools. GPU-Z logs sensor data, spotting faulty readings. For intermittent spins, use Event Viewer in Windows to check error logs tied to GPU events. Thermal imaging cameras reveal hot spots, but for home users, software suffices.
Common pitfall: Ignoring driver conflicts, always clean install.
Compare tools in this table:
| Tool | Best For | Free/Paid | Ease for Beginners |
| MSI Afterburner | Fan curves & monitoring | Free | Medium |
| GPU-Z | Detailed specs & logs | Free | Easy |
| HWInfo | Comprehensive system scan | Free | Advanced |
| FurMark | Stress testing | Free | Easy |
This helps choose based on need.
When to Replace Your GPU Fans?
If software fixes and basic cleaning don’t help, the GPU fans may have failed. Common signs include fans not spinning even at maximum manual speed or grinding noises before they stop completely.
In such cases, you can replace the fans by buying matching models, often available on marketplaces like eBay. This usually requires disassembling the GPU, which can void the warranty, followed by swapping the fans and reapplying thermal paste.
For water-cooled systems, switching to an AIO cooling kit can be an alternative. Replacement fans typically cost $20–50 per fan, so it’s worth comparing the expense with upgrading to a newer GPU if the card is already old.
For related cooling issues, you may also want to read CPU Fan Not Spinning – Quick Fixes & Causes.
How to Prevent GPU Fan Problems in the Future:
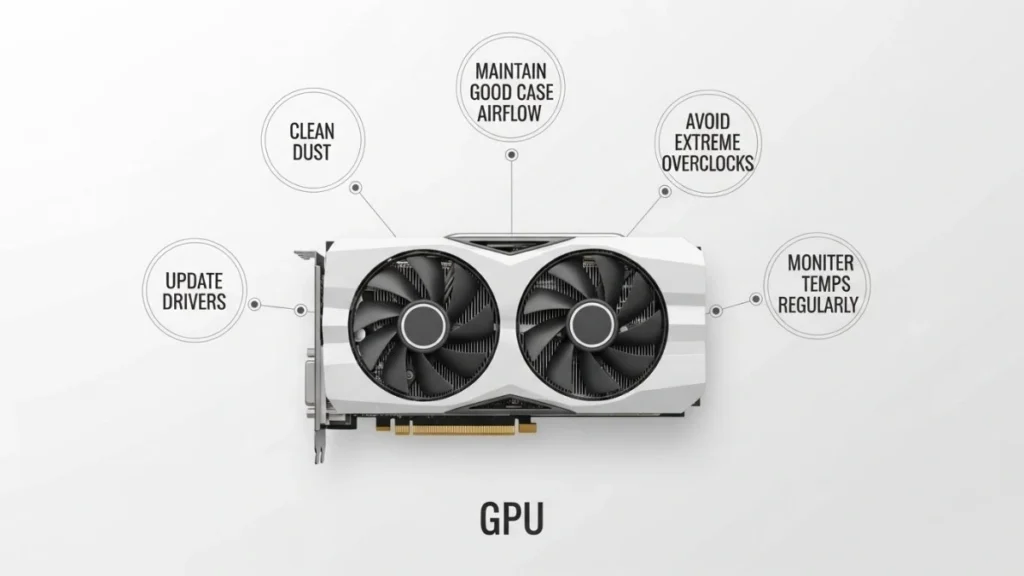

- Clean dust every 3–6 months using compressed air.
- Maintain good case airflow, add intake fans.
- Update drivers monthly for bug fixes.
- Avoid extreme overclocks without custom cooling.
- Monitor temperatures regularly to catch sudden rises early.
These simple habits can significantly extend your GPU’s lifespan. In dusty environments, using dust filters helps a lot.
You can also reduce heat by undervolting the GPU, which lowers temperatures and reduces long-term fan wear.
Finally, don’t overlook room temperature. Keeping ambient temperatures below 25°C can noticeably improve cooling performance.
AMD vs. NVIDIA: Fan Management Differences
AMD’s Adrenaline offers granular tuning, like hysteresis to prevent rapid on/off.
NVIDIA’s app focuses on auto-optimization, but is less flexible without third-party tools.
Table comparison:
| Feature | AMD | NVIDIA |
| Zero RPM Toggle | Easy in Adrenaline | Via partners like MSI |
| Curve Customization | Detailed sliders | Basic in app, advanced in Afterburner |
| Software Integration | Radeon-specific | GeForce Experience |
For GPU usage tips, check GPU Usage So High on Windows? Easy Fixes That Work (2026).
Real-Life Examples: User Stories
A gamer using an RTX 4080 noticed the fans staying silent while playing Fortnite. The issue turned out to be Zero RPM mode, which was resolved by adjusting fan settings in MSI Afterburner, resulting in a temperature drop of around 10°C.
An office user with an RX 6700 XT experienced crashes when the GPU fans stopped spinning. In this case, heavy dust buildup was blocking airflow, and a proper cleaning along with reapplying thermal paste solved the problem.
In another case shared on forums, a PC builder initially suspected dead GPU fans, but the real issue was a loose power cable. Reseating the cable fixed the boot issue and restored display output.
These examples show that most GPU fan issues have simple explanations when basic checks are done first. A common mistake is panicking and attempting risky fixes like baking the GPU, which is often unnecessary and can cause permanent damage.
FAQs:
1. What if my GPU fans spin briefly on boot then stop?
This is normal. GPUs test fans at startup and stop them if temperatures are low.
2. Can bad thermal paste cause fans not to spin?
Not directly, but poor paste can cause temperature or sensor issues.
3. Is it safe to run without fans spinning?
Only at idle. Under load, fans must spin to avoid overheating.
4. How do I know if my PSU is the issue?
Test with a known working PSU and check recommended wattage.
5. Can a GPU fan be fixed, or does it always need replacement?
Sometimes cleaning or reseating cables works. Dead fans need replacement.
Conclusion:
GPU fans not spinning is often normal due to Zero RPM mode, but it shouldn’t be ignored under load. Most issues come down to software settings, dust buildup, or loose connections, and can be fixed with basic checks. By monitoring temperatures and maintaining proper airflow, you can avoid long-term damage and keep your GPU running smoothly.